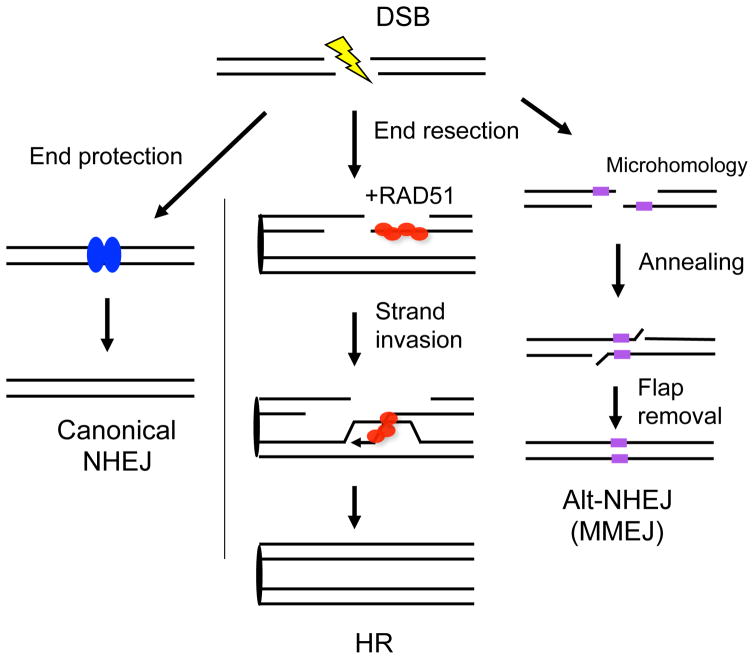
Figure 2. Multiple pathways to repair DSBs.
Canonical NHEJ is operational throughout the cell cycle. It can protect DNA ends prior to ligation, but deletions and insertions can occur, especially if the ends are frayed. HR is a relatively precise pathway to repair DSBs, the defining step of which is strand invasion catalyzed by RAD51. RAD51 forms a nucleoprotein filament on single-stranded DNA formed by end resection. The 3′ invading end primes repair DNA synthesis from the homologous template, primarily the sister chromatid. End resection is also an intermediate step in alternative-NHEJ (alt-NHEJ) involving microhomology, i.e., a few bp of sequence identity between the DNA ends. For this reason, it is also termed microhomology-mediated endjoining (MMEJ). If single-stranded DNA forms containing longer stretches of complementarity, they can also anneal, in which case the pathway is termed single-strand annealing (SSA, not shown).