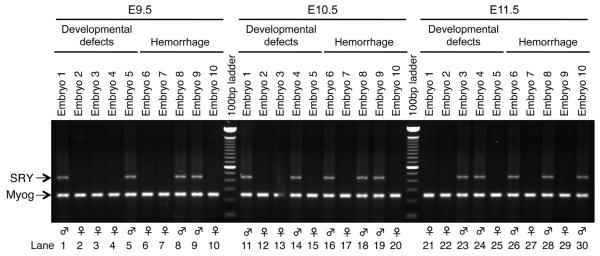
Figure 3. Variability in a phenotype of Cre;myr-p110α embryos is not associated with X-chromosome inactivation.
PCR products were generated from purified gDNA of the yolk sacs dissected from embryos harvested from CMV-Cre homozygous mother and myr-p110αwt/fl father crosses. Embryos with either developmental defects (lanes 1 to 5 at E9.5, 11 to 15 at E10.5, and 21 to 25 at E11.5) or hemorrhage (lanes 6 to 10 at E9.5, 16 to 20 at E10.5, and 26 to 30 at E11.5) were randomly chosen at E9.5 to E11.5 at which embryonic lethality is occurring. There was no evident difference between female and male in either viability or phenotypic variability. The genomic PCR products were visualized in a 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis. Representative results of PCR detecting 441 bp of male-specific gene SRY and 245 bp of the autosomal gene myogenin (Myog) found in both males and females.