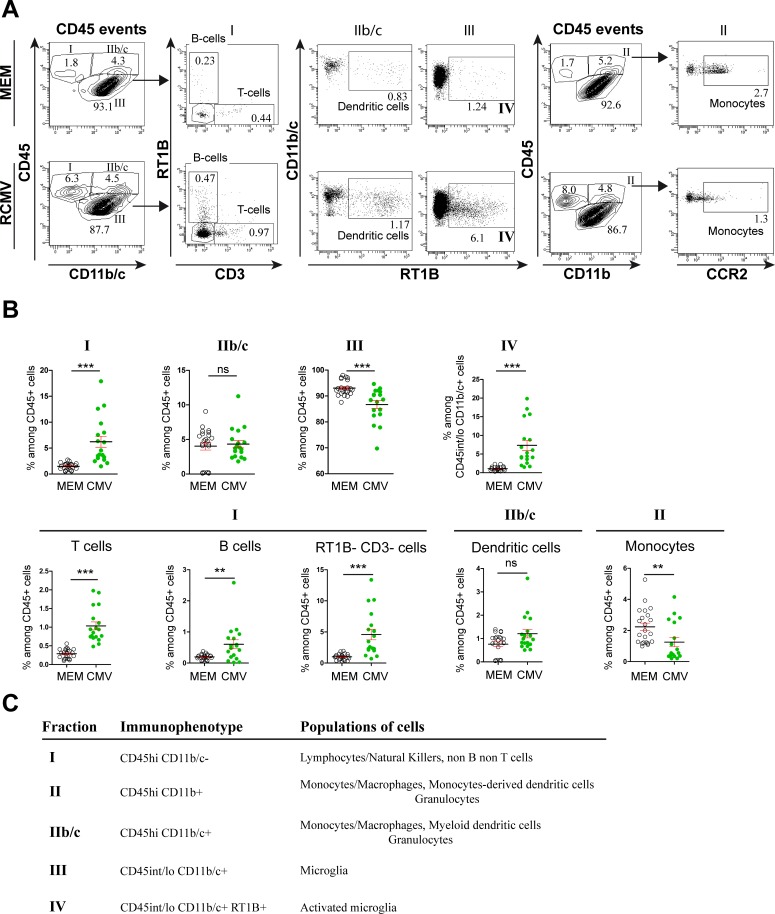
Fig 5. Flow cytometry analysis of leukocytes collected at P1 from RCMV-infected brains.
Total leukocytes (CD45 events) were gated for CD45 and either Cd11b/c or CD11b expressions and further characterized for CD3 and RT1B or for CCR2 expressions, respectively (A) Representative flow cytometry plots in control (MEM-injected) brains and (RCMV) brains. (B) (top) The distribution of fractions I and III, but not IIb/c, as defined according to CD45/CD11b/c expression status, was significantly different in CMV-infected brains as compared with control (MEM) brains at P1. Cells from fraction III (microglia) were further characterized in either conditions according to RT1B expression status, allowing to determine the proportion of activated microglia (fraction IV). The proportion of activated microglia increased significantly in the infected brains at P1 (bottom) Cells from fraction I were further characterized in either conditions according to CD3 and RT1B expression status, allowing to distinguish between T cells, B cells and non-B non-T cells. The proportions of T cells, B cells and non-B non-T cells increased significantly in CMV-infected brains at P1. Dendritic cells from fraction IIb/c were characterized in either conditions according to RT1B expression status whereas monocytes were characterized in either conditions according to CD45/CD11b (corresponding to fraction II) and CCR2 expression status. The proportions of monocytes increased significantly in CMV-infected brains at P1. No difference in the proportion of dendritic cells was observed in the infected brains at P1. All analyzes were performed using 18 (RCMV) and 22 (control condition) brains, respectively. Values are means ± SEM. The statistical significance of the observed variation in frequency in each cell population is indicated. Mann Whitney test, two tailed; ns: non significant; **: p < 0.01; ***: p < 0.001 (C) Fractions of cells as defined according to their respective immunophenotypes and the cell populations they correspond to, are indicated.