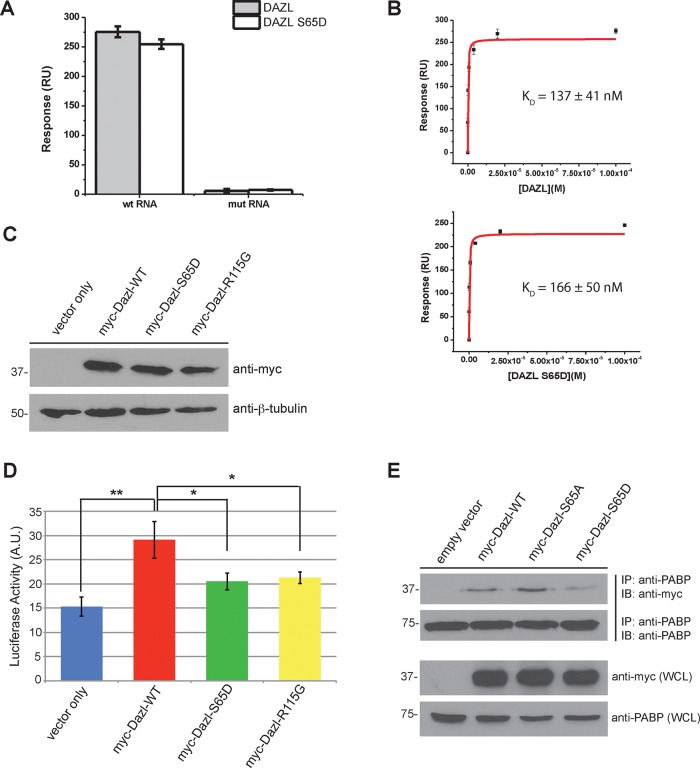
FIGURE 3:
Mutation of Dazl S65 impairs translation but not RNA binding. (A) Bar chart depicting relative binding responses of wild-type and S65D Dazl-RRM proteins to wild-type and mutant (i.e., nonspecific control) RNAs. (B) Equilibrium binding plots of the interaction of wild-type and mutant Dazl-RRM proteins interacting with the wild-type RNA sequence. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Error bars represent one SD. (C) Expression of myc-tagged Dazl-WT, Dazl-S65D, and Dazl-R115G by immunoblotting of whole-cell lysates from transfected HeLa cells. (D) Reduced translation of a Dazl target upon expression of Dazl-S65D. HeLa cells were cotransfected with psiCHECK-2-SYCP3-3′UTR (a characterized Dazl-binding sequence cloned downstream of the sequence encoding Renilla luciferase) and the indicated Dazl constructs. Cells were lysed, and luciferase activity was quantified. Average of three independent experiments. Error bars indicate SD. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.005 as calculated by a Student’s t test. (E) Diminished binding of PABP to Dazl upon phosphomimetic mutation of S65. HEK293 cells were cotransfected with plasmids encoding PABP and pCMV-myc (empty vector), myc-Dazl-WT, myc-Dazl-S65A, or myc-Dazl-S65D. Cells were lysed, followed by immunoprecipitation of PABP and immunoblotting of the precipitated material with the indicated antibodies. Western blots shown are representative of three independent experiments. IB, immunoblot; IP, immunoprecipitate; WCL, whole-cell lysate.