Fig. 1.
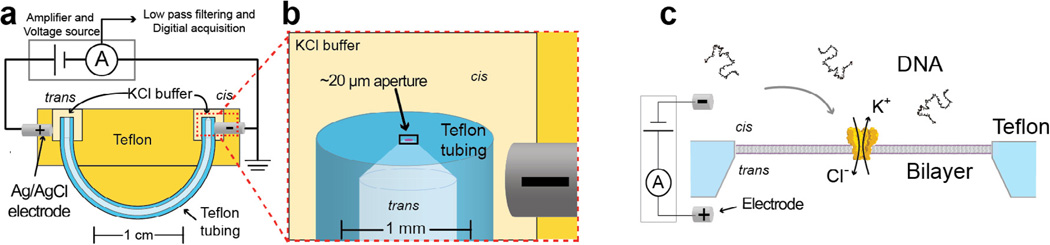
Schematic of the u-tube bilayer setup at various scales (originally described by Akeson et al. in 1999 [2], see Appendix A for detail on building and setting up such an experiment). The bilayer is established across the ~20 µm aperture. Once a bilayer is established, MspA is added to the cis solution until a single pore inserts. Once the operator detects an insertion, the remaining MspA is perfused from the cis well and the system is prepared for experiments. When a voltage is applied across the bilayer by two Ag/AgCl electrodes (as shown in c, not to scale), negatively charged DNA is drawn into and through the pore. While all experiments described below are performed using this single channel recording setup, it is possible to massively parallelize nanopore setups for higher throughput. Figure modified from [37].