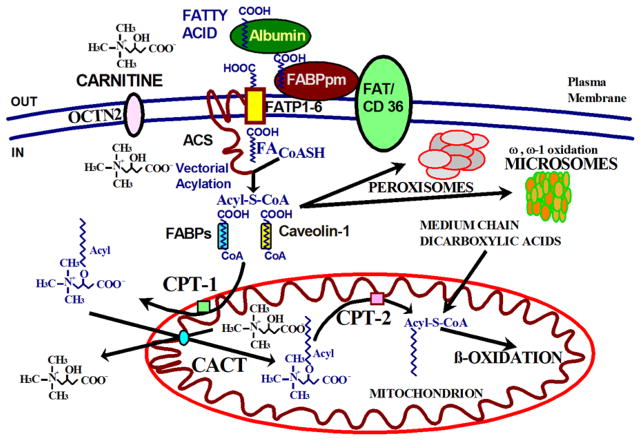
FIGURE 2. The carnitine cycle in fatty acid oxidation.
Fatty acids bound to albumin are transferred across the plasma membrane by the action of fatty acid transport proteins (FATP), fatty acid translocase (FAT/CD36), caveolins and plasma membrane fatty acid binding proteins (FABPpm). Inside the cell, fatty acids undergo vectorial acylation, a process catalyzed by acyl-CoA synthases (ACS), that traps them in the cytoplasm as acyl-CoA thioesters. The acyl-CoA thioesters are then conveyed through different metabolic pathways in mitochondria, peroxisomes and microsomes based on the cell energy status. ACS: acyl-CoA synthases; CACT: carnitine acyl carnitine translocase; CPT-1: carnitine palmitoyl transferase-1; CPT-2: carnitine palmitoyl transferase-2; FA: fatty acid; FABPpm: plasma membrane fatty acid binding proteins; FAT/CD36: fatty acid translocase; FATP: fatty acid transport proteins; OCTN2: organic cation transporter novel 2.