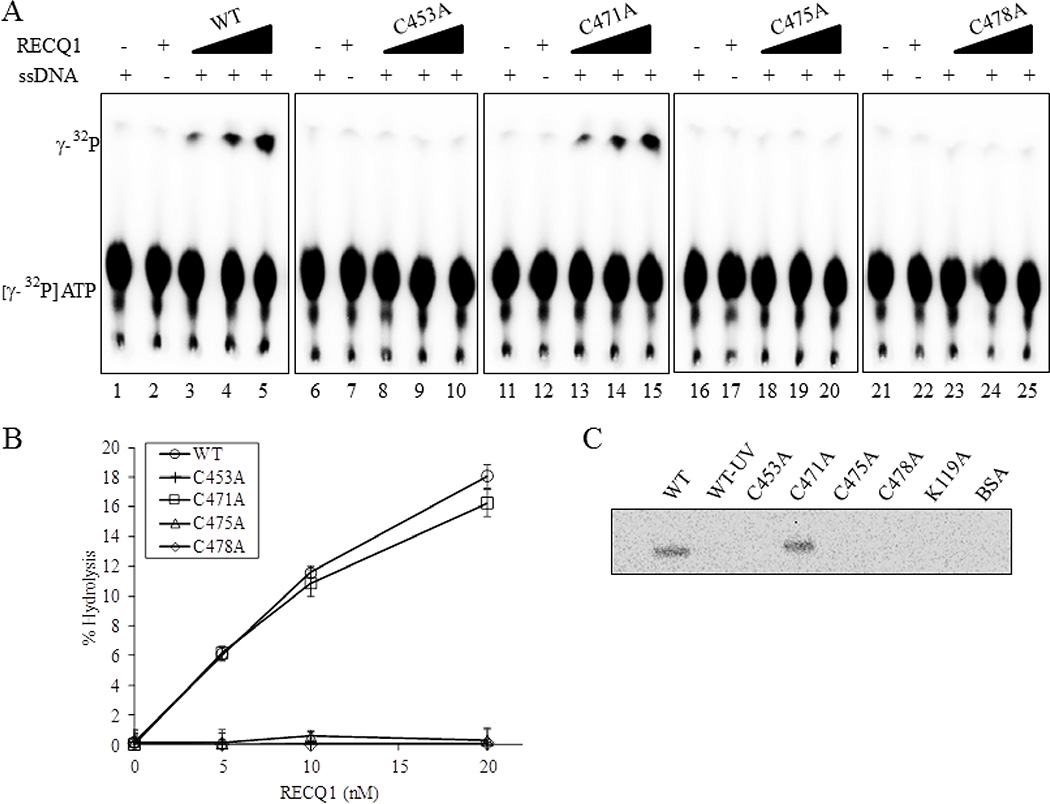
Figure 3. ZBD mutants RECQ1-C453A, RECQ1-C475A and RECQ1-C478A are ATPase deficient.
(A) Representative thin-layer chromatography showing dose-dependent ATPase activity of wild-type and ZBD mutants of RECQ1. RECQ1 proteins (5, 10 and 20 nM) in ATPase assay mixture containing radiolabelled γP32-ATP, cold ATP in the absence or presence of single strand DNA were incubated for 30 min at 37°C followed by autoradiography. Lanes 1, 6, 11, 16, 21 are no enzyme controls; lanes 2,7,12, 17, 22 are no single strand DNA controls. (B) Quantitative comparison of ATPase activity of wild-type and cysteine mutants. The average values are presented with SDs indicated by error bars from triplicate assays. (C) ATP binding activity of wild-type and mutant RECQ1 proteins. One microgram of the wild-type or mutant helicase protein was incubated with [γ-32P] ATP in the presence of fixed concentration of single strand DNA and increasing concentrations of proteins was UV cross-linked as described in Materials and Methods. Following SDS-PAGE electrophoresis, gel was visualized using a PhosphorImger.