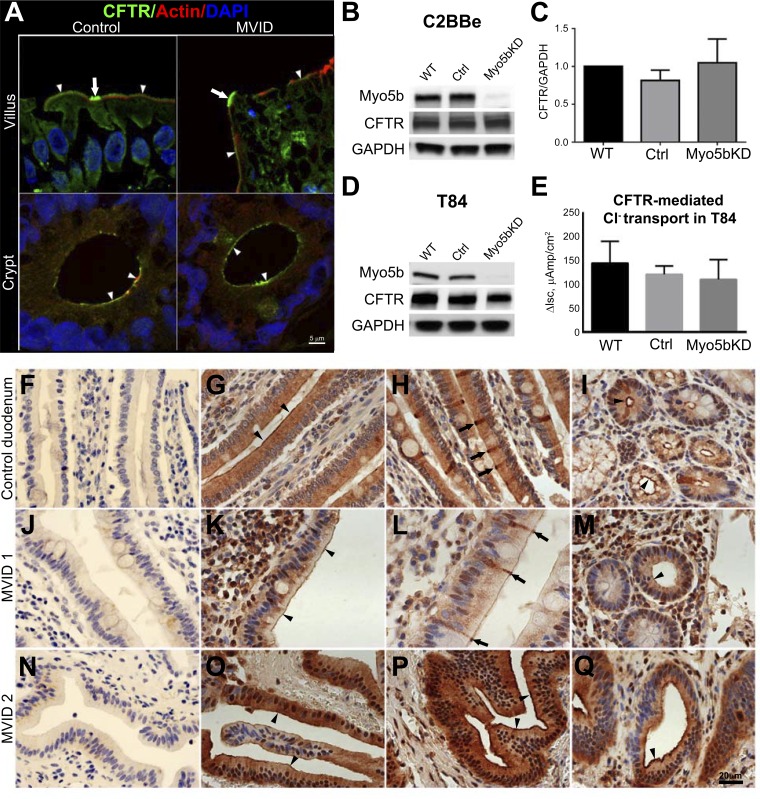
Fig. 6.
CFTR localization, expression, and ion transport in the human duodenum, C2BBe, and T84 cells. A: confocal microscopy images of CFTR (green) IFL in cryosections of normal and MVID human duodenum are shown in relation to F-actin (red); nuclei are stained in blue. Arrowheads indicate BB IFL; arrows indicate CFTR High Expressor (CHE) cells. Scale bar, 5 μm. B: immunoblot analysis of Myo5b and CFTR in lysates of mature polarized C2BBe cells relative to GAPDH. C: comparison of GAPDH-corrected CFTR expression in mature polarized C2BBe cells. D: immunoblot analysis of Myo5b and CFTR in lysates of mature polarized T84 cells relative to GAPDH. Cells were analyzed following Isc measurements. E: CFTR short-circuit delta current (ΔIsc) measurements in the polarized T84 cells. Cl− secretion was stimulated with forskolin and inhibited with CFTR(inh)-172 inhibitor. F–Q: immunohistochemical localization of CFTR in normal and MVID human intestine. Horseradish peroxidase staining detects CFTR in small intestine sections from paraffin-embedded blocks of normal control (G–I) and two independent nongenetically characterized but confirmed MVID patients, MVID 1 (J–M), and MVID 2 (N–Q). F, J, and N are controls for negative staining. Nuclei are stained blue. Scale bar 25 μm. G: staining of CFTR in the BB (arrowheads) and supranuclear cytoplasm of villus enterocytes. H: intense BB and subapical CFTR staining in villus CHE cells (arrows). I: apical CFTR staining in crypt (black arrowheads). K: BB CFTR stain (arrowheads). L: intense BB and subapical CFTR staining in villus CHE cells (arrows). M: apical CFTR stain in crypt. O–Q: IHC stain for CFTR in MVID 2. O–P: BB (arrowheads) and subapical stain for CFTR. Q: apical CFTR stain in crypt (arrowhead).