Fig. 1.
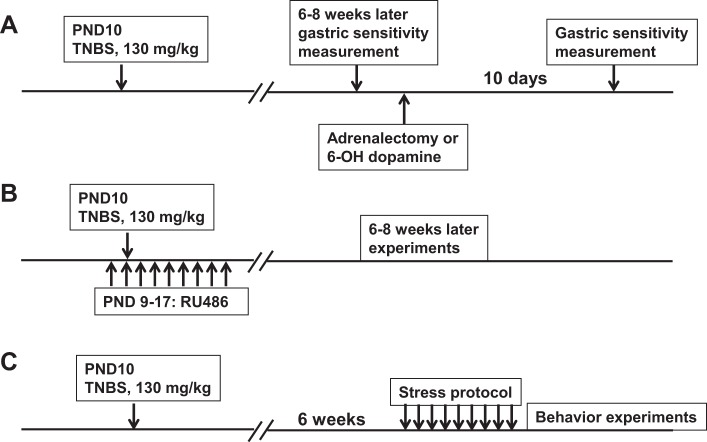
Time line of experimental protocols. A: trinitrobenzenesulfonic (TNBS) was used to induce colonic inflammation on postnatal day (PND) 10. Later (6–8 wk), gastric sensitivity was measured, and the gastric hypersensitivity (GHS) rats were assigned to one of three groups: 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) treatment, sham surgery, and bilateral adrenalectomy (n = 8 each). Later (10 days) gastric sensitivity was measured again in each group of rats. B: TNBS inflammation was induced on PND 10, as above (n = 5). In addition, these rats were treated once a day with 16 mg/kg RU-486 from PND 9 to 17 to block the glucocorticoid receptor. Experiments were performed 6–8 wk later. C: adult GHS rats subjected previously to TNBS neonatal colon inflammation on PND 10, and age-matched controls (control, n = 6; GHS, n = 9; and GHS + RU-486, n = 10) were subjected to 9-day heterotypic intermittent chronic stress protocol; experiments were performed 24 h after the end of the stress protocol.