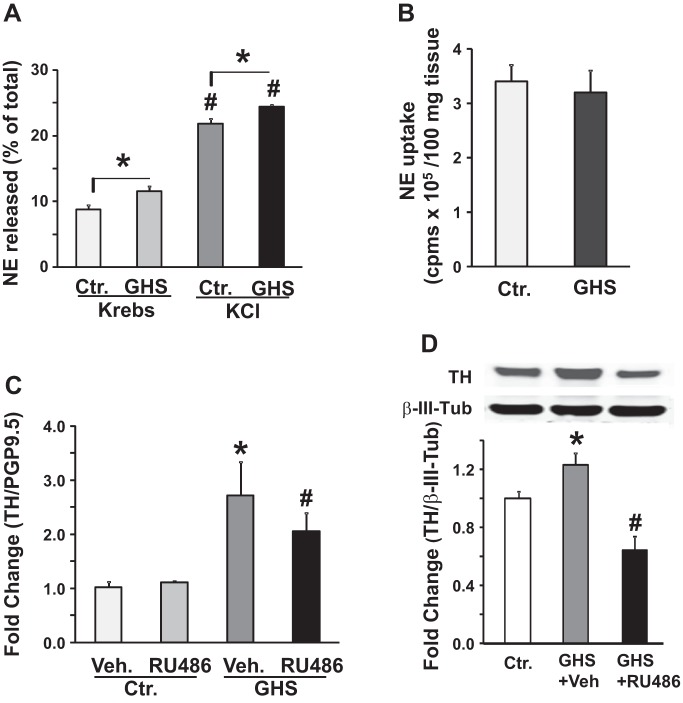
Fig. 4.
Gastric NE release and tyrosine hydroxylase expression in the celiac ganglia of control (Ctr.) and gastric hypersensitive (GHS) rats. A: bar graph shows NE release in the presence of reuptake and monooxygenase inhibitors from the fundus muscularis externa isolated from GHS and Ctr. rats in Krebs or high KCl Krebs. KCl Krebs significantly increased NE release in the fundus tissues from both Ctr. and GHS rats (n = 5, #P < 0.05). NE release was significantly greater in tissues from GHS vs. Ctr. rats in Krebs as well as in KCl Krebs (n = 5, *P < 0.05). B: bar graphs show no significant difference in NE uptake, expressed as cpms/100 mg tissue, by fundus muscularis externa strips between Ctr. and GHS rats (n = 5, P > 0.05). C: bar graph shows the levels of Th mRNA expression normalized to protein gene product (PGP9.5) in the celiac ganglia of adult Ctr. and GHS rats that were treated with RU-486 during the neonatal period. RU-486 treatment did not significantly alter Th mRNA expression in Ctr. rats (n = 6, P > 0.05). Th mRNA expression was significantly greater in GHS rats vs. vehicle treated Ctr. rats (n = 6, *P < 0.05). Neonatal treatment with RU486 significantly decreased Th mRNA expression in GHS rats (n = 6, #P < 0.05). D: Western blot panel and bar graph show tyrosine hydroxylase expression in the celiac ganglia extracts from Ctr. (n = 6), GHS (n = 9) and GHS+RU486 (n = 10) rats. TH expression in the celiac ganglia was significantly greater in GHS + vehicle rats vs. Ctr. rats (*P < 0.05). Neonatal RU-486 treatment significantly suppressed TH expression in the celiac ganglia of GHS rats (#P < 0.05).