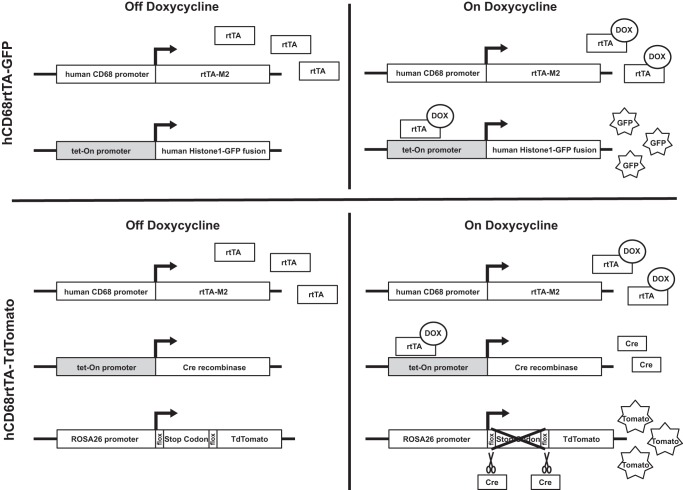
Fig. 1.
hCD68-rtTA reporter mice. Two strains of reporter mice were used to assess hCD68-rtTA activation in this study: hCD68rtTA-GFP and hCD68rtTA-TdTomato. Both mice express the hCD68-rtTA transgene, where a fragment of the human CD68 promoter drives expression of rtTA-M2 (rtTA). Even without doxycycline, rtTA is expressed by all cells that activate the human CD68 promoter. When doxycycline is administered, it binds to rtTA and this complex can activate tet-responsive promoters (shown in grey). In hCD68rtTA-GFP mice the combination of rtTA and doxycycline directly activates expression of GFP. In hCD68rtTA-TdTomato mice the combination of rtTA and doxycycline leads to production of the enzyme Cre recombinase (Cre). It indirectly activates expression of TdTomato (tomato); Cre cleaves a floxed stop codon at the start site of TdTomato, after which tomato expression is driven by the ubiquitously activated Rosa26 promoter.