Fig. 1.
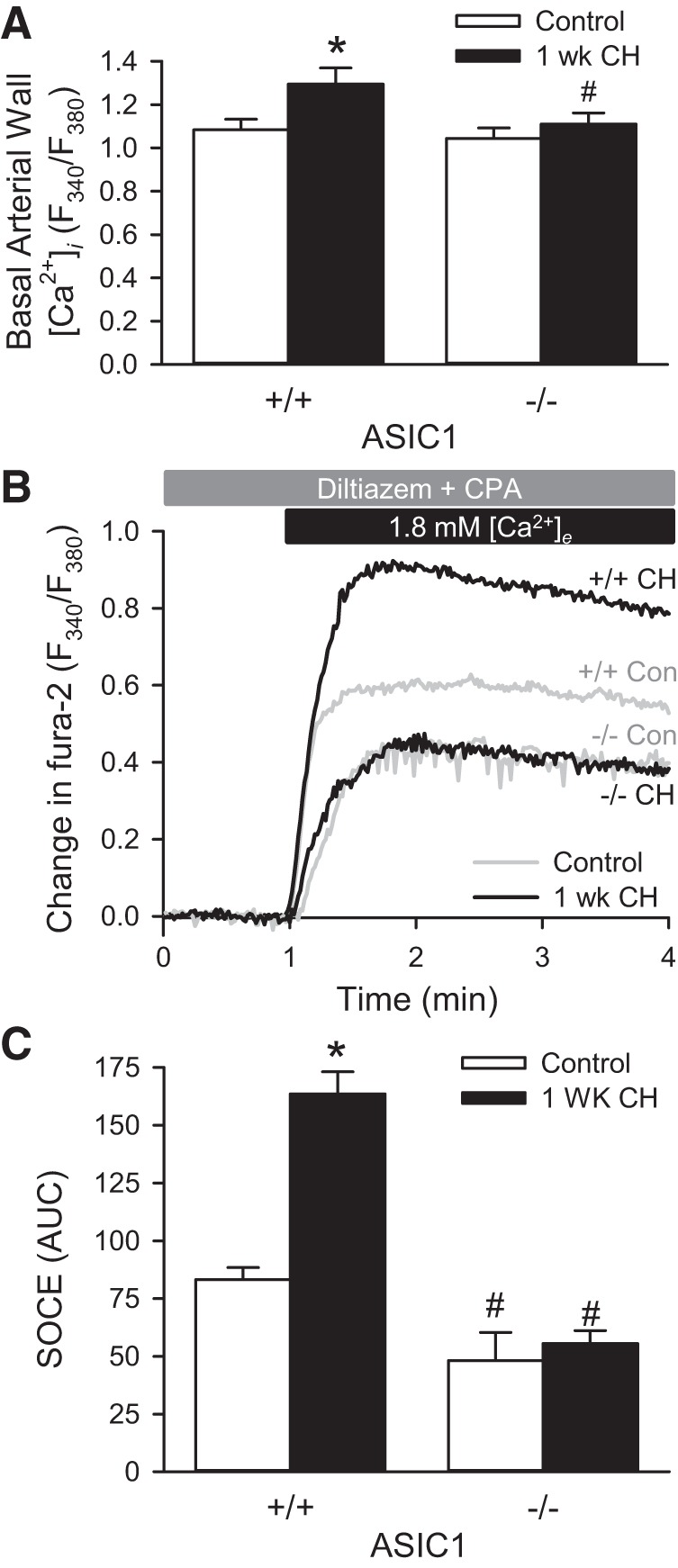
Chronic hypoxia (CH)-induced increases in basal pulmonary arterial intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) and store-operated calcium entry (SOCE) are ASIC1 dependent. A: basal arterial wall [Ca2+]i ratios (F340/F380) in small pulmonary arteries from control and CH (1 wk) ASIC1 wild-type (+/+) and knockout (−/−) mice. B: averaged change in fura-2 ratio (F340/F380) upon repletion of 1.8 mM extracellular Ca2+ ([Ca2+]e). C: summary data showing SOCE as area under curve (AUC) in small pulmonary arteries from control and CH-exposed (1 wk) ASIC1 wild-type (+/+) and knockout (−/−) mice. SOCE experiments were performed in the presence of cyclopiazonic acid (CPA, 10 μM) and diltiazem (50 μM). Values are means ± SE; n = 7–10 animals/group. *P < 0.05 vs. control mice, #P <0.05 vs. ASIC1+/+ mice analyzed by a two-way ANOVA and individual groups compared with the Student-Newman-Keuls test.
