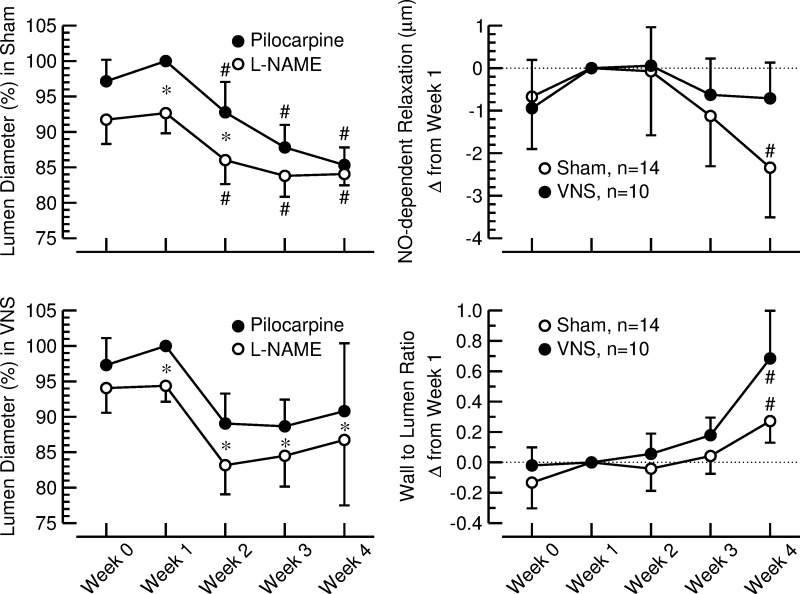
Fig. 4.
Left: lumen diameter of the long posterior ciliary artery (LPCA) after corneal application of a 1% pilocarpine solution (●) and after corneal application of a 4% l-NAME solution (○). Values are expressed as a percentage of the values measured after pilocarpine application at week 1 when stimulators were off (means ± SE). Top, sham-stimulated animals (n = 14). Bottom, rats with VNS (n = 10). *P < 0.05, pilocarpine vs. l-NAME. #P < 0.05 vs. week 1. Right: nitric oxide (NO)-dependent relaxation (top) and wall-to-lumen ratio (bottom) of the LPCA assessed by in vivo imaging in sham-stimulated rats (sham; ○) and animals with vagal nerve stimulation (VNS; ●). Values are changes from week 1 (means ± SE). #P < 0.05 vs. week 1.