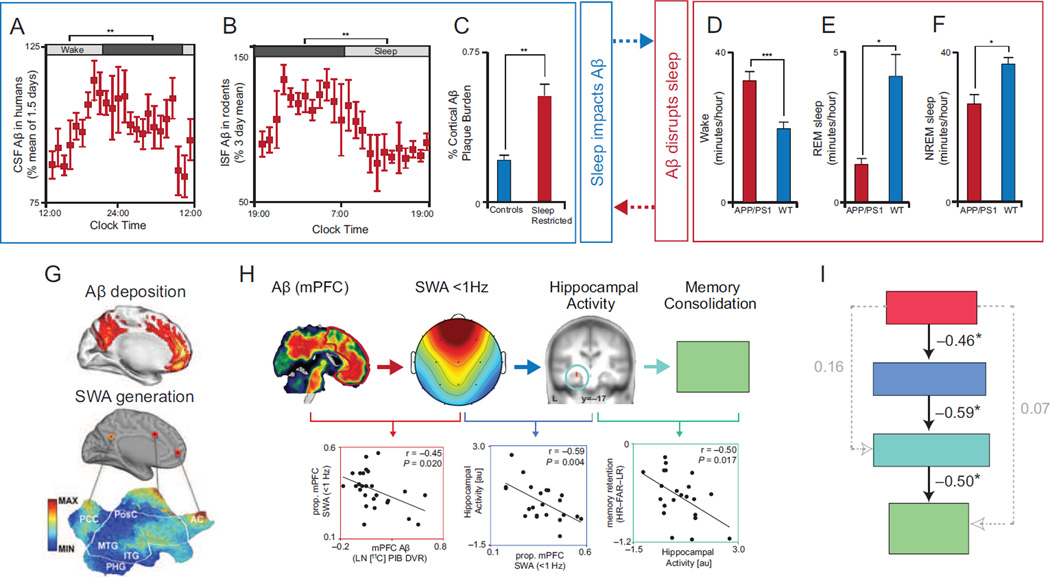
Figure 1.
Reciprocal relationship between Aβ and Sleep, and their influence on hippocampus-dependent memory consolidation. CSF Aβ in humans (a) and ISF Aβ in rodents (b) rise during wake and fall during sleep, and sleep restricting APP/PS1 mutant rodents results in higher cortical Aβ plaque burden (c; adapted from25). Further, APP/PS1 mutant rodents (red bars) exhibit increased wake time (d) and reduced REM (e) and NREM (f) sleep time relative to wild type rodents (blue bars; adapted from26). These findings represent a reciprocal relationship between sleep and Aβ: sleep and sleep disturbance can influence Aβ accumulation (a–c, blue box), while Aβ aggregation can disrupt sleep and increases wake time (d–f, red box). A potential mechanism underlying disrupted NREM SWS by Aβ pathology is the aggregation of Aβ (g, top sagittal brain slice adapted from48) within the same medial prefrontal cortical nodes critical for the electrical source generation of NREM slow waves (g, bottom sagittal brain slice adapted from47). Indeed, medial prefrontal Aβ burden predicts the degree of disrupted <1Hz NREM SWA (h, red scatter plot, adapted from21). The disruption of <1Hz NREM SWA by Aβ, in turn, is associated with impaired sleep-dependent consolidation of hippocampus-dependent memory. Disrupted <1Hz NREM SWA is associated with reduced overnight development of hippocampus-independent retrieval (h, blue scatter plot), that normally fosters superior memory stabilization and thus remembering (h, turquoise scatter plot). These interactions are further supported by structural equation modeling, which revealed that the only significant path linking Aβ pathology to impaired hippocampus-dependent memory was through its intermediary disruption of <1Hz NREM SWA (i, adapted from21). While the relationship between Aβ and NREM SWA is likely to be bidirectional, the strongest link between Aβ and memory was through its association with NREM SWA. Abbreviations: Aβ, amyloid-β protein; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; ISF, interstitial fluid; APP/PS1, amyloid precursor protein and presenilin 1 mutant rodents; SWA, slow wave activity; MAX, maximum; MIN, minimum; PCC, posterior cingulate cortex; PosC, post-central gyrus; MTG, medial temporal gyrus; ITG, inferior temporal gyrus; PHG, parahippocampal gyrus; AC, anterior cingulate gyrus; mPFC, medial prefrontal cortex; prop., proportion; LN, natural logarithm; DVR, distribution volume ratio; L, left hemisphere; HR, hit rate; FAR, false alarm rate; LR, lure rate; au, arbitrary units; and HC, hippocampus.