Figure 6.
Gfra1/2 Play Important Roles for the Heart Development In Vivo
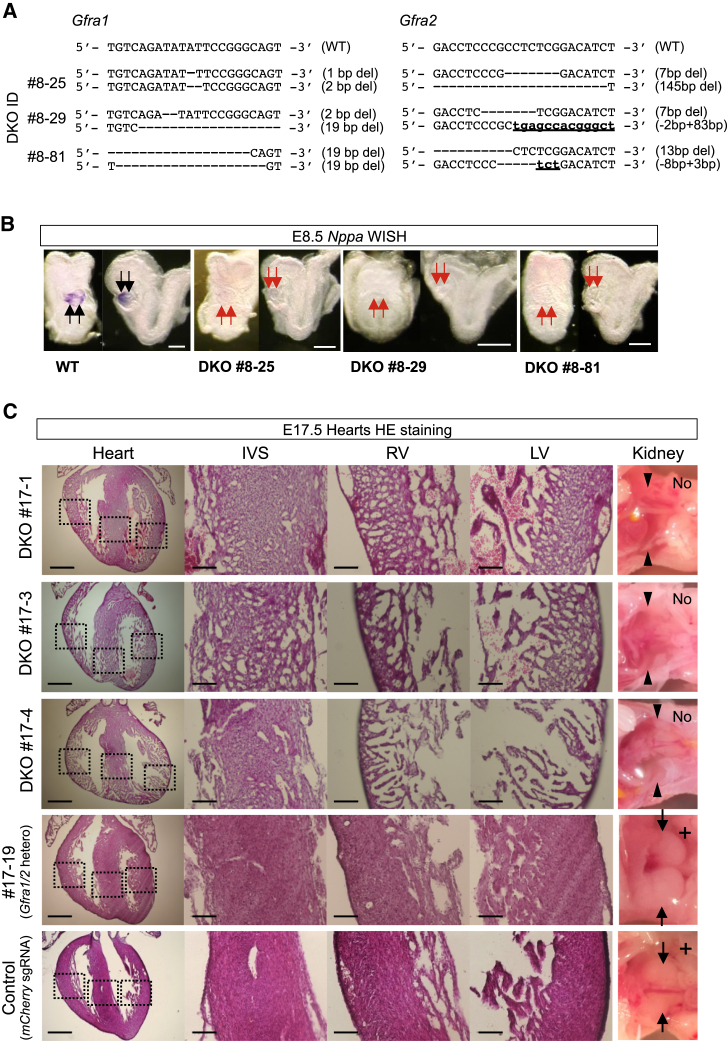
(A) Genotype of the Gfra1/2 DKO mouse embryos generated by the direct injection of Gfra1-targeted sgRNA, Gfra2-targeted sgRNA, and Cas9 mRNA into zygotes.
(B) WISH analyses of differentiated cardiomyocyte marker Nppa in Gfra1/2 DKO and WT littermate embryos at E8.5. Nppa expressions disappeared in DKO embryos (red arrows). Scale bar, 250 μm.
(C) H&E staining for the hearts of Gfra1/2 DKO E17.5 embryos. The compaction layers of myocytes were thin, and the alignments of cardiomyocytes were impaired in Gfra1/2 DKO embryos as compared to the control hearts (mCherry sgRNA and Cas9 mRNA transduced embryos) and Gfra1/2 compound heterozygote mutant. Gfra1 null resulted in kidney agenesis as previously described (black arrowheads, No), whereas the well-developed kidney was observed in the heterozygotes and WT (black arrows, +) (Enomoto et al., 1998). The mutation of each embryo induced by CRISPR/Cas9 is shown in Figure S7B.
IVS, intraventricular septum; RV, right ventricle; LV, left ventricle. Scale bar, 500 μm in whole-heart images and 100 μm in higher magnification. See also Figure S7.