Figure 2.
“Stop” Codons in C. magnum and Parduczia sp.: Either Sense or Stop Codons
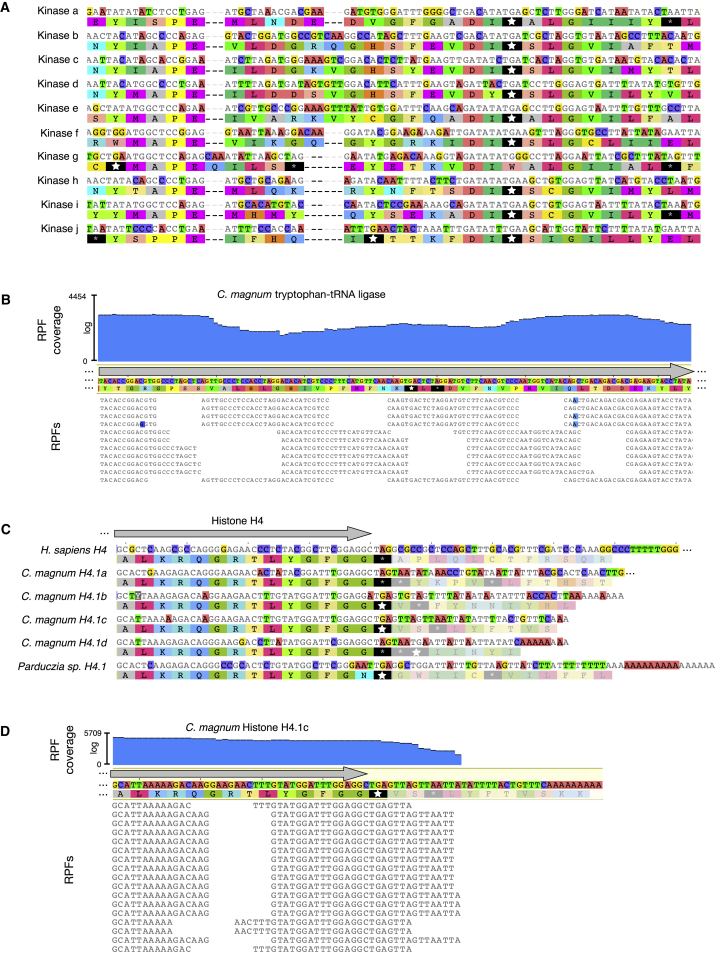
(A) C. magnum protein kinase alignment region highlighting putative sense “stop” codons. Standard genetic code stop codons are shown with stars, with larger stars for UGA. MMETSP0210 IDs: CAMNT_0008311047, CAMNT_0008316317, CAMNT_0008295895, CAMNT_0008281491, CAMNT_0008274923, CAMNT_0008274561, CAMNT_0008271577, CAMNT_0008291651, CAMNT_0008280967, CAMNT_0008289329.
(B) Ribosome-protected fragments (RPFs) mapped to a C. magnum tryptophan-tRNA ligase transcript (Data S1AC and S1AD). “RPF coverage” is calculated from all the bases of 25–32 nt RPFs.
(C) Histone H4 C-termini and stop codons (gray arrow, coding sequence) from C. magnum, Parduczia sp., and Homo sapiens. Poly(A) tails are visible at C. magnum and Parduczia sp. mRNA 3′ termini. Histone H4.1a– H4.1d: MMETSP0210 IDs: CAMNT_0008274265, CAMNT_0008297091, CAMNT_0008284521, and CAMNT_0008296393; Parduczia sp. histone H4 is MMETSP137 CAMNT_0047598059. H. sapiens histone H4 is GenBank: M16707.1. Judging from paired-end read mapping, the 3′ UTR of H4.1a is incorrectly fused to a downstream transcript.
(D) RPFs mapped to histone H4.1c (Data S1AE and S1AF).
See also Figure S2.