Figure S2.
Related to Figure 3
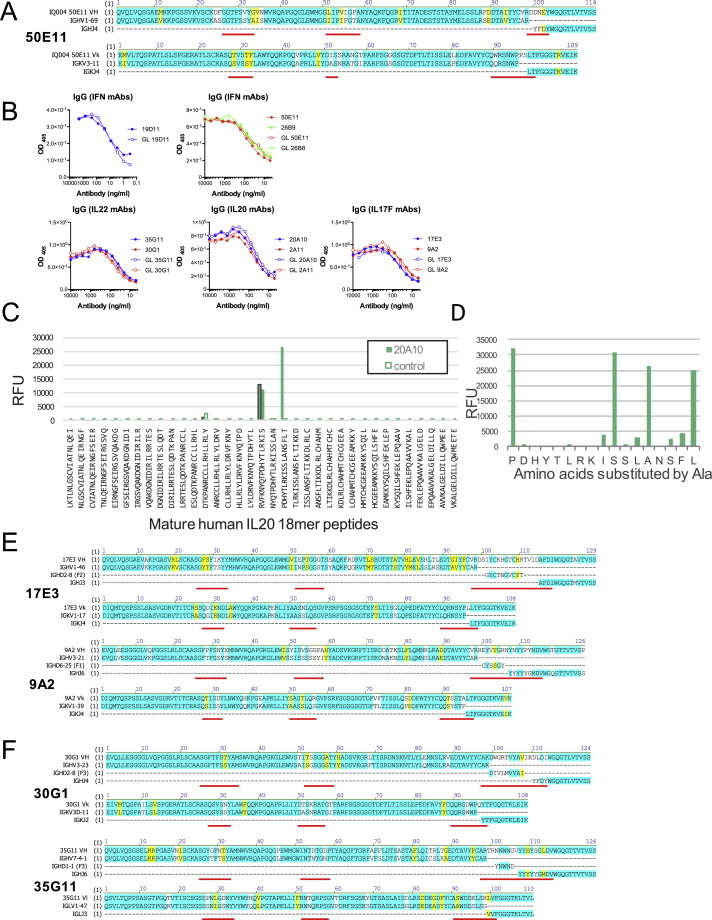
(A) Corresponding closest germlines and heavy chain diversity regions of APS1 patient-derived mAb 50E11 targeting IFNαs.
(B) IgG concentration of APECED/APS1 derived mAbs and its closest germline antibodies as measured by ELISA.
(C) Mapping of the epitope of the patient-derived anti-IL20 antibody 20A10 by primary peptide array. The antibody specifically binds to the peptide comprising amino acids P101 to T118. Signals at the 18-mer peptides starting with R93 and D73 are caused by binding of the detection antibody as shown in the control.
(D) Alanine-scan of the epitope comprising residues P101 to L117. Alanine substitutions at positions D102, H103, Y104, T105, L106, R107, K108, S111, N114, S115, and F116 lead to a breakdown of mAb binding.
(E and F) Corresponding closest germlines and heavy chain diversity regions of APS1 patient-derived mAbs. (E) anti-IL17F mAbs. (F) anti-IL22 mAbs. Identical amino acids are highlighted in blue, mutated but similar amino acids in yellow and CDRs are underlined in red.