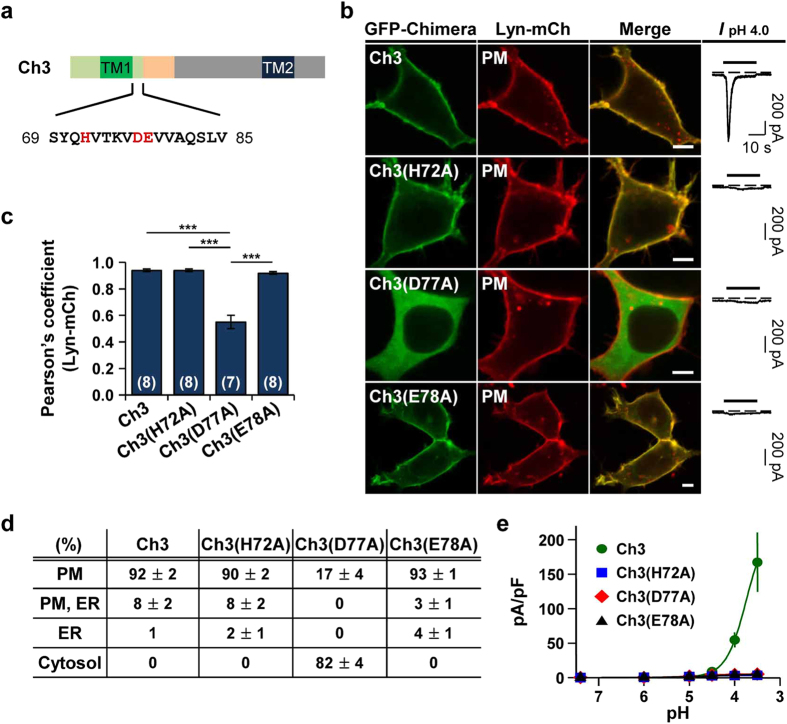
Figure 5. H72 and E78 are critical for proton-sensitivity, whereas D77 is involved in determining subcellular localization and proton-sensitivity.
(a) Putative proton-binding sites (H72, D77, and E78) located in the proximal post-TM1 domain of Ch3 were highlighted in red. (b) Left, representative confocal images of HEK293T cells expressing each chimera with the plasma membrane marker, Lyn-mCh. The scale bar represents 5 μm. Right, pH 4.0-induced currents measured from the cells expressing each chimera. Dashed line indicates the zero current level. (c) Pearson’s correlation coefficient between the plasma membrane marker and each chimera (mean ± SEM, ***p < 0.001, with one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test). The number on each bar indicates n for each condition from three independent experiments. (d) Percentage of cells showing each chimera in specific subcellular localizations (mean ± SEM). For each chimera, 250 cells were counted from five independent experiments. (e) pH-dependent peak current density of each chimera (mean ± SEM). The time interval between pH applications is 2 min for a complete recovery from desensitization (Ch3, n = 5; Ch3(H72A), n = 5; Ch3(D77A), n = 6; Ch3(E78A), n = 5).