Fig. 2.
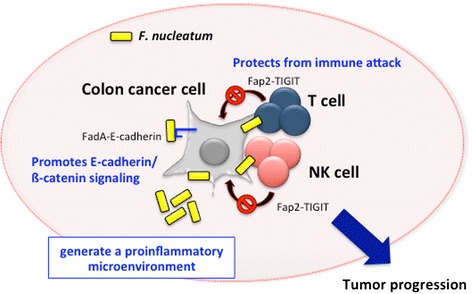
Involvement of F. nucleatum in colon cancer development. Figure shows the mechanisms of F. nucleatum in the involvement of colon cancer. F. nucleatum promotes E-cadherin/ß-catenin signaling via FadA adhesin and protects from immune attack by engaging its bacterial protein Fap2 with the inhibitory immunoreceptor TIGIT on NK and T cells. Moreover, F. nucleatum generate a proinflammatory microenvironment through the recruitment of tumor-infiltrating immune cells
