Figure 4.
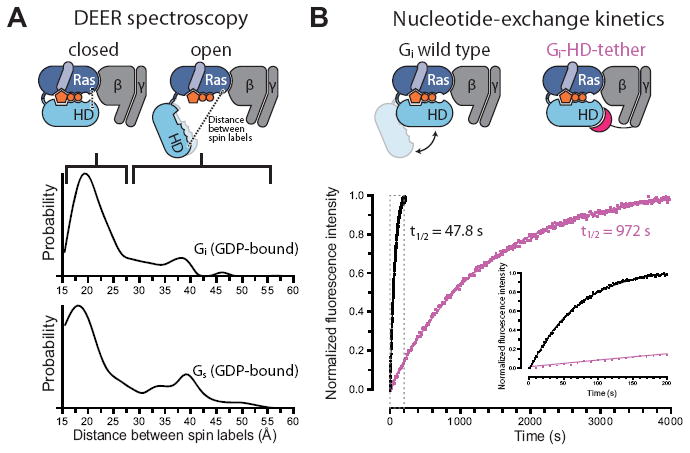
Experimental validation of spontaneous Gα domain separation in GDP-bound heterotrimeric G proteins and its role in nucleotide exchange. (A) DEER distance distributions measured between spin labels attached to the Ras and helical domains of Gi (Glu238 and Arg90) and Gs (Asn261 and Asn112) show multiple distance peaks, consistent with an equilibrium between closed and open conformations of the α subunit in the presence of GDP, despite the absence of an activated receptor. These distance distributions extend to much larger values than would be expected if the G proteins maintained their crystallographic nucleotide-bound conformations (Fig. S15). (B) Domain separation impacts the basal GDP release rate. The Gi-HD-tether construct (Fig. S16), designed to restrict domain separation, exchanges nucleotides 20-fold more slowly than Gi wild type, under conditions where GDP release is rate-limiting. GDP release was monitored by BODIPY-GTPγS binding kinetics, shown for Gi wild type (black) and Gi-HD-tether (purple). The inset corresponds to the gray dashed box.
