Figure 1.
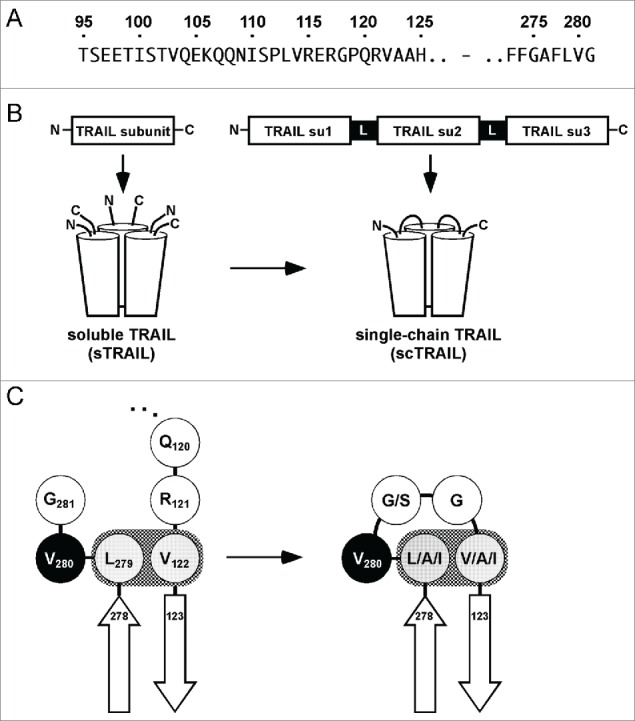
A single-chain format for human TRAIL. (A) Amino acid sequences in the extracellular domain of human TRAIL in which the modifications described in this work are located. For the previous generation of scTRAIL, we used the N-terminal position 95 as a start, involving 26 aa residues of the stalk region, preceding the receptor binding domain. Each individual TRAIL subunit of the scTRAIL molecules described in this work begins in close proximity of the N-terminus of the receptor binding domain (122–281), as realized for the aa positions 118, 120, 121, 122 and 123. (B) Scheme depicting the generation of single-chain TRAIL from soluble TRAIL. Su, subunit. (C) Val122 and Leu279 of human TRAIL are involved in a hydrophobic interaction, thereby defining beginning and end of the TNF homology domain. Both residues were connected by Val280 and 2 linking residues as demonstrated for scTRAIL-FLVGGVA and derived variants scTRAIL-F(L/A/I)V(G/S)G(V/A/I)A in order to form scTRAIL molecules of minimal size.
