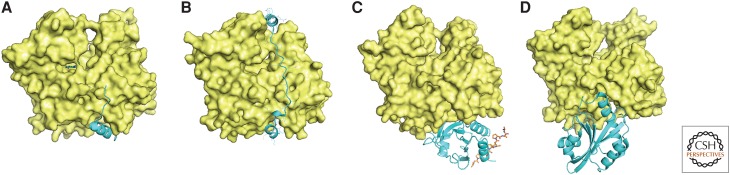
Figure 5.
Proteins that bind actin monomers. Space-filling models of the actin monomer with ribbon diagrams of bound proteins. This is the standard view of actin (see Fig. 1), with the ATP-binding cleft at the top and the barbed-end groove at the bottom. (A) The WH2 helix binds in the barbed-end groove (PDB: 3M1F, from Vibrio parahaemolyticus Vopl). (B) Thymosin-β4 helices bind in both the barbed-end groove and across the pointed-end cleft (PDB: 4PL7). (C) Profilin can bind simultaneously to the barbed end of actin and to polyproline helices such as that from vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP), shown here as a red stick figure (PDB: 2PBD). (D) The carboxy-terminal cofilin domain from twinfilin binds on the barbed end of the actin molecule (PDB: 3DAW).