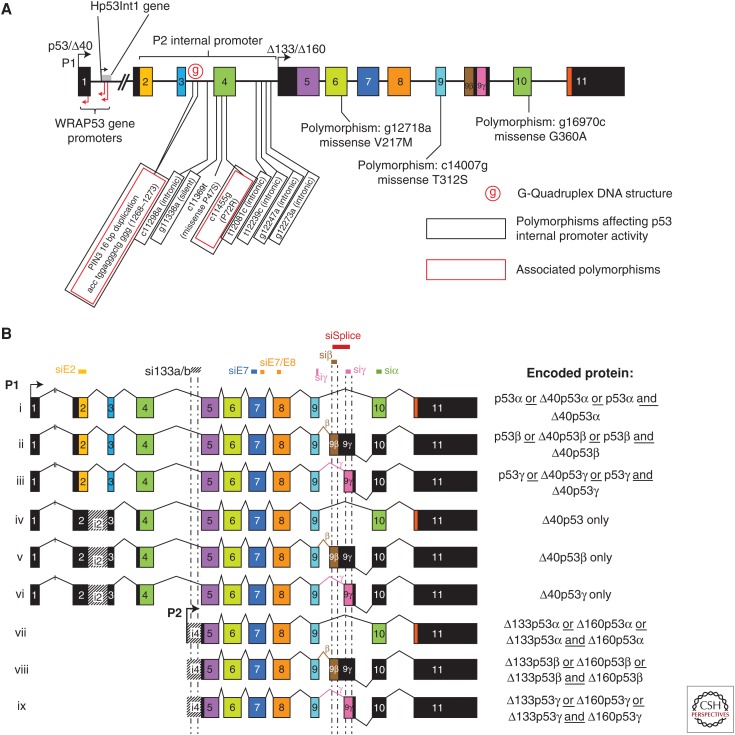
Figure 1.
TP53 locus and p53mRNAs. All introns/exons are represented to scale. Black boxes represent noncoding sequences, whereas coding sequences are colored. (A) The human TP53 gene’s locus structure. The TP53 gene, which is composed of 11 exons and two cryptic exons (9β and 9γ), encodes several p53 isoforms attributable to alternative promoters (↱ P1 and P2) and alternative retention of the cryptic exons. The noncoding exon-1 and intron-1 contain different promoters for the WRAP53 gene (antisense-coded) and intron-1 contains the Hp53Int1 gene. A G-quadruplex DNA structure located within intron-3 modulates splicing of intron-2 and activities of the internal p53 promoter P2. Several polymorphisms (including Pin3 and R72P) change activities of the internal p53 promoter (P2). (B) p53 mRNAs. The TP53 gene encodes nine different mRNAs attributable to the alternative promoters (↱ P1 and P2) and splicing (^). The promoter P1, located upstream of exon-1, encodes for intron-2 spliced (i, ii, and iii) or intron-2 retained (iv, v, and vi) mRNAs. The intron-2 spliced mRNAs can encode the full length (ATG1) and/or the Δ40 (ATG40) proteins, depending on the cell context, whereas the mRNA retaining intron-2 can only encode the Δ40 proteins. The P2 initiation transcription site is located in intron-4 and encodes for three transcripts (vii, viii, and ix), which encode the Δ133 and the Δ160 forms. Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) targeting the different p53 isoforms are represented on top of the corresponding exons or introns.