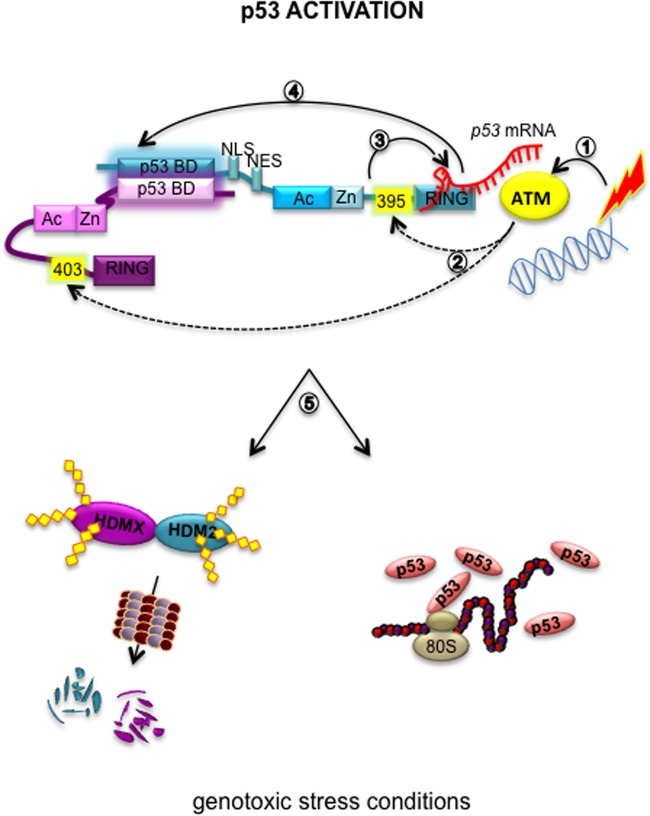
FIG 6.
Proposed model of the allosteric effects on the HDM2-HDMX heterodimer by p53 mRNA. p53 mRNA binding on HDM2 promotes an allosteric change that allows p53 activation. (1) Under genotoxic stress conditions ATM is activated. (2) ATM phosphorylates HDM2(S395) and HDMX(S403). (3) The phosphorylation of S395 allows p53 mRNA binding to the RING domain. (4) The p53 mRNA interaction opens up a new binding site between HDMX and HDM2 in the N-terminal region in a RING-RING-independent manner. (5) These events allow the proper ubiquitination of HDMX and HDM2 itself to ensure the p53 stabilization and activation after DNA damage. Dotted lines represent ATM-dependent phosphorylations.