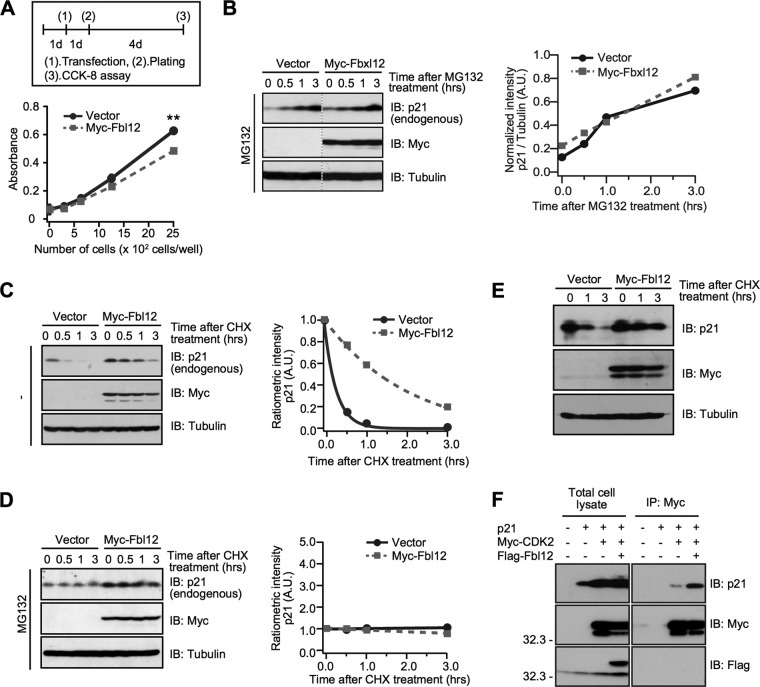
FIG 3.
Fbl12 suppresses default degradation of p21. (A) HEK 293 cells were transfected with either control or Myc-Fbl12 plasmids. The cellular proliferation was analyzed using the Cell Counting Kit-8 (n = 3; means ± SEM; **, P < 0.01 by Student's t test). (B, left) HEK 293 cells were transfected with either Myc-Fbl12 or control vector. Cells were incubated with 20 μM MG132 for the indicated times and were then subjected to immunoblot analyses. (Right) Data were quantified using ImageJ software. These data are representative of three independent experiments. (C, left) HEK 293 cells were transfected with either Myc-Fbl12 or control vector. Cells were incubated in the absence or presence of 50 μg/ml cycloheximide (CHX) for the indicated times and were then subjected to immunoblot analyses. (Right) Data were quantified by using ImageJ software. These data are representative of three independent experiments. (D, left) HEK 293 cells were transfected with either Myc-Fbl12 or control vector. Cells were incubated in the absence or presence of 50 μg/ml CHX together with 20 μM MG132 for the indicated times and were then subjected to immunoblot analyses. (Right) Data were quantified using ImageJ software. These data are representative of three independent experiments. (E) HEK 293 cells were transfected with the indicated vectors. Cells were incubated in the absence or presence of 50 μg/ml CHX for the indicated times and were then subjected to immunoblot analyses. (F) Coimmunoprecipitation of Flag-Fbl12, p21, and Myc-CDK2 in HEK 293 cells. Ectopic expression of Fbl12 promoted the association of p21 with CDK2.