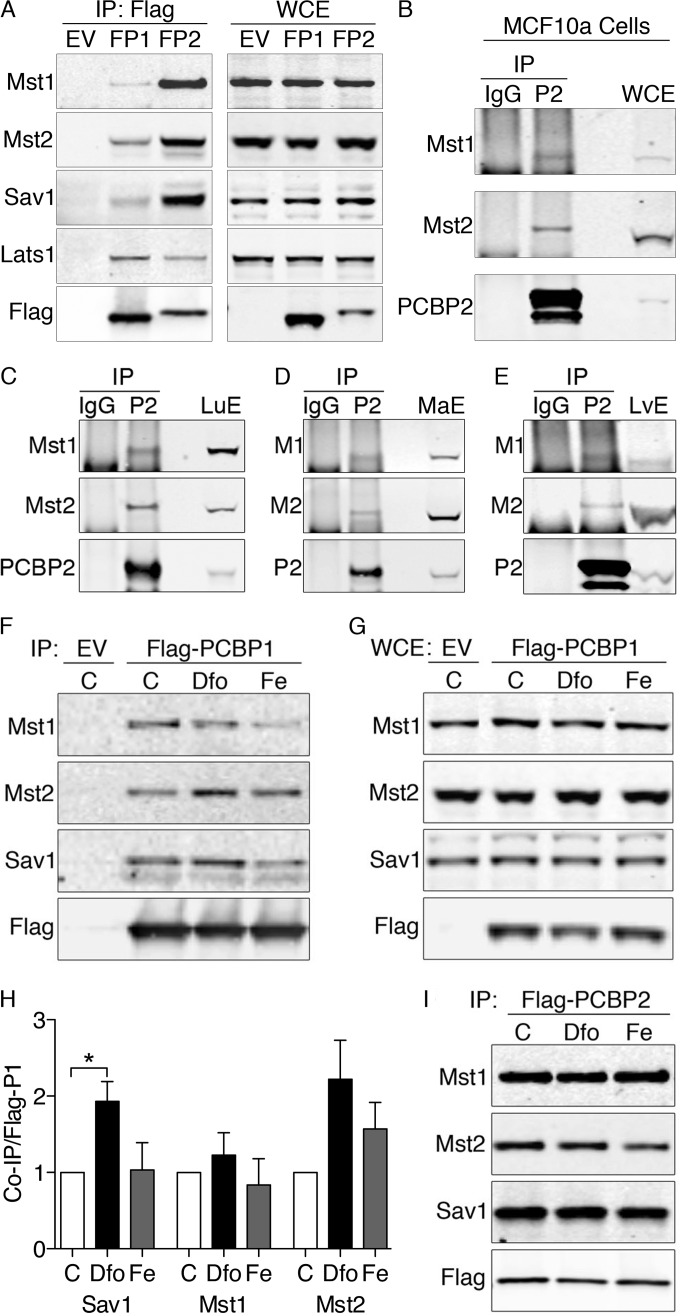
FIG 1.
Physical interactions between Hippo signaling complex, PCBP1, and PCBP2 in human cells and murine tissues. (A) Physical interactions between PCBP1, PCBP2, and Hippo components in HEK293 cell lines. HEK293 stable cell lines containing empty vector (EV), inducible Flag-PCBP1 (FP1), or Flag-PCBP2 (FP2) were induced for 18 h. The lysates were subjected to IP with anti-Flag resin, and immune complexes (IP: Flag) and whole-cell extracts (WCE) were examined by Western blotting using antibodies against Mst1, Mst2, Sav1, total Lats1 (tLats1), and Flag. (B) Physical interactions between PCBP2 and the Hippo complex in MCF10A cells. MCF10A cell lysates were subjected to IP with anti-PCBP2 antibody or normal mouse IgG. Immune complexes and WCE were examined by Western blotting for Mst1, Mst2, and PCBP2. Sav1 is not detectable due to the interference of IgG heavy chain. Experiments were replicated three times. (C to E) Binding of Mst1 and Mst2 to PCBP2 in lung and liver. Mouse lung extracts (C), mammary gland extracts (D), and liver extracts (E) were subjected to IP with anti-PCBP2 and normal mouse IgG. Immune complexes and tissue extracts (LuE, MaE, and LvE) were analyzed by Western blotting for Mst1 and Mst2. (F to I) Effects of iron supplementation or chelation on binding of Hippo components to PCBPs. Cells expressing Flag-PCBP1 (F and G) or Flag PCBP2 (I) were treated overnight with iron (Fe) (100 μg/ml) or the iron chelator Dfo (100 μM). The lysates were subjected to IP and Western blotting as for panel A. (H) Quantitation of Hippo components coprecipitated with Flag-PCBP1. Experiments were replicated three times; *, P < 0.05. The error bars indicate SEM.