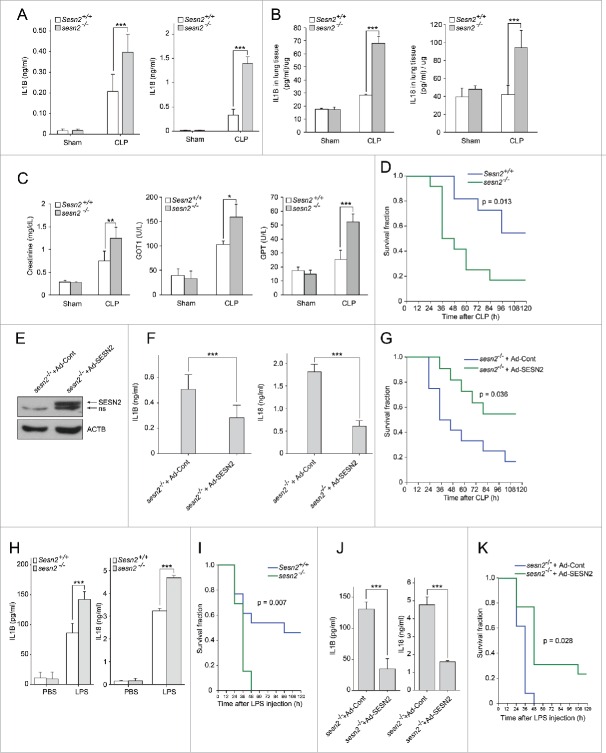
Figure 7.
Sesn2 plays a protective role against septic shock in mouse sepsis models. (A-D) Sepsis was induced by CLP in Sesn2+/+ and sesn2−/− mice. (A) Serum IL1B and IL18 as measured by ELISA (n = 5), (B) IL1B and IL18 in homogenized lung tissues as measured by ELISA (n = 5), (C) serum creatinine, GOT1 and GPT (n = 5) 24 h after CLP surgery, and (D) survival of Sesn2+/+(n = 11) mice or sesn2−/−(n = 12) mice. (E-G) CLP was performed in Sesn2+/+ and sesn2−/− mice. (E) Immunoblot analysis for SESN2 in liver tissue lysates from sesn2−/−+ Ad-Cont and sesn2−/−+ Ad-SESN2; ‘ns’ indicates a nonspecific band. (F) Serum IL1B and IL18 as measured by ELISA (n = 5) 24 h after CLP surgery, and (G) survival of sesn2−/−+ Ad-Cont (n = 13) or sesn2−/−+ Ad-SESN2 (n = 13). (H and I) Sesn2+/+ and sesn2−/− mice were challenged with LPS. (H) Serum IL1B and IL18 as measured by ELISA 24 h after LPS challenge (12 mg/kg, i.p.) and (I) Survival of Sesn2+/+(n = 13) mice or sesn2−/−(n = 13) mice after LPS challenge (25 mg/kg, i.p.). ((J)and K) sesn2−/−+ Ad-Cont and sesn2−/−+ Ad-SESN2 mice were challenged with LPS. (J) Serum IL1B and IL18 as measured by ELISA 24 h after LPS challenge (12 mg/kg, i.p.) and (K) survival of sesn2−/−+ Ad-Cont (n = 13) or sesn2−/−+ Ad-SESN2 (n = 13) mice after LPS challenge (25 mg/kg, i.p.). Data shown are the mean ± s .e.m. The survival rates were analyzed by Kaplan-Meier log-rank test. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.005 from an ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test.