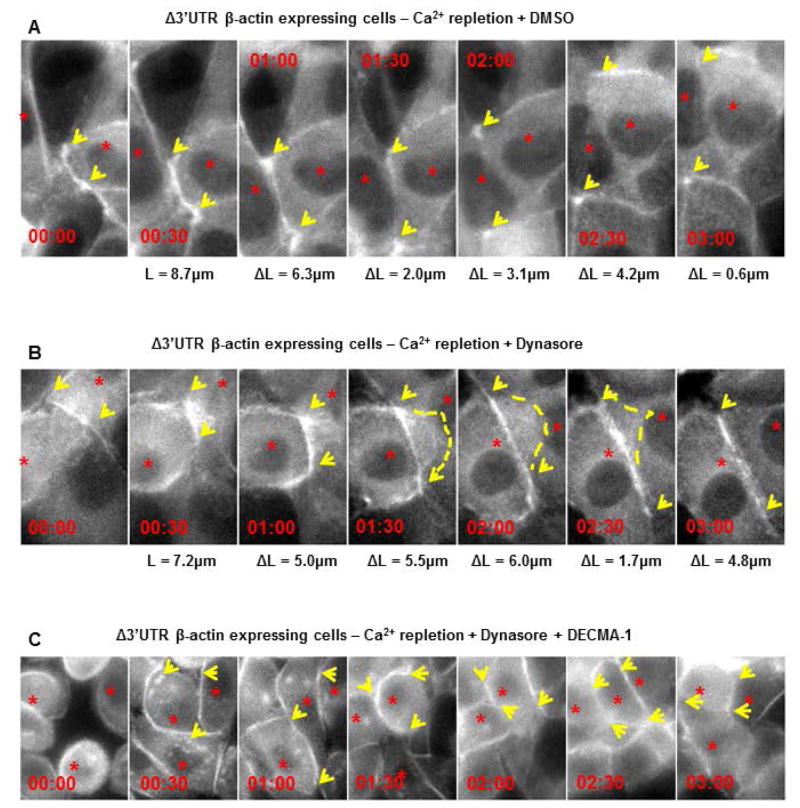
Figure 4. Blocking endocytosis and E-cadherin function are both required for rescuing adherens junction assembly in cells with partially mislocalized β-actin translation.
Montage of MDCK cells with partially mislocalized β-actin translation (expressing Δ3′UTR β-actin mRNA that encodes an eGFP-fusion tag), following calcium repletion. Cells were treated with: (A) 0.5% (v/v) DMSO or (B) 80μM Dynasore or (C) 80μM DMSO + 100μg/mL DECMA-1, following calcium repletion. Time is indicated as duration post initial contact (hh:mm). L is an estimate of contact length and ΔL represents the increase in length with respect to the previous frame. Arrows point to expanding contacts. Note in cells treated with DMSO, there is overlap of neighboring cells while in cells treated with 80μM dynasore, contact expansion is followed by retraction of the protrusion (dotted line). Treating cells with DECMA-1 completely abolishes contact expansion as seen by the lack of continued expansion of the filamentous actin along the cell-cell interface. The data represents qualitative assessment of retraction followed by contact expansion upon inhibition of endocytosis in cells expressing Δ3′UTR β-actin mRNA following calcium repletion. Three independent experiments were performed for each condition in A, B and two independent experiments for C.