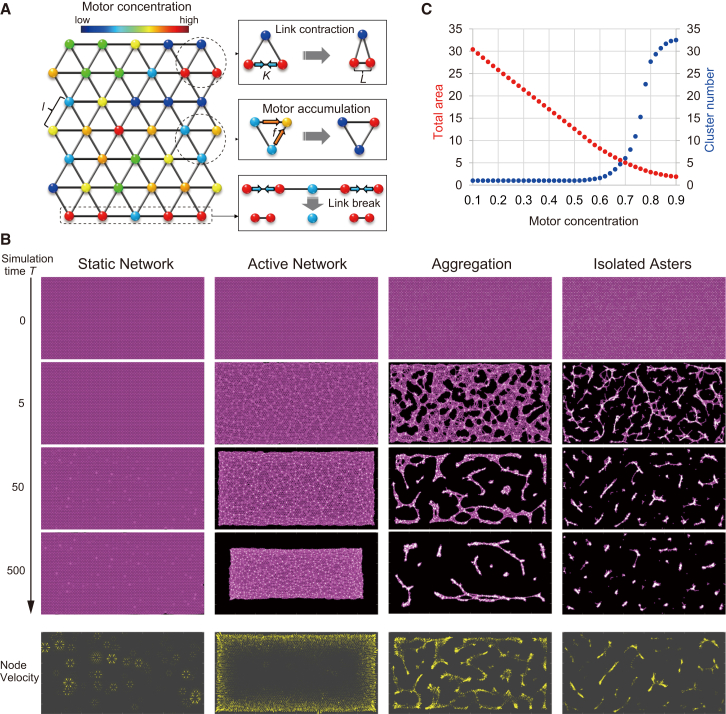
Figure 5.
Coarse-grained model of the filament motor system. (A) Schematic representations of the model and its dynamic rules. Two adjacent active nodes contract with each other with strength K. Motors accumulate against the concentration gradient with flux f. A link is severed when it is elongated above a threshold length Lc. The motor concentration at each node is represented by the color spectrum. (B) Spatiotemporal dynamics of the model for different motor concentrations (Cub) and the parameters K and f. (Cub, K, f) = (0.1, 15, 0.01), (0.4, 15, 0.01), (0.7, 15, 0.01), and (0.9, 30, 0.02) for the static network, active network, aggregation, and isolated cluster, respectively. Links are depicted by magenta lines and motors are depicted by white circles. Node velocities at T = 50 are shown by yellow arrowheads, sized in proportion to the velocity magnitude. (C) Total areas (red) and cluster numbers (blue) measured at T = 500 are displayed as a function of the motor concentration. (K, f) = (15, 0.01). Circles denote the mean value for 100 repeated simulations, starting with randomized initial distributions of the motor concentration.