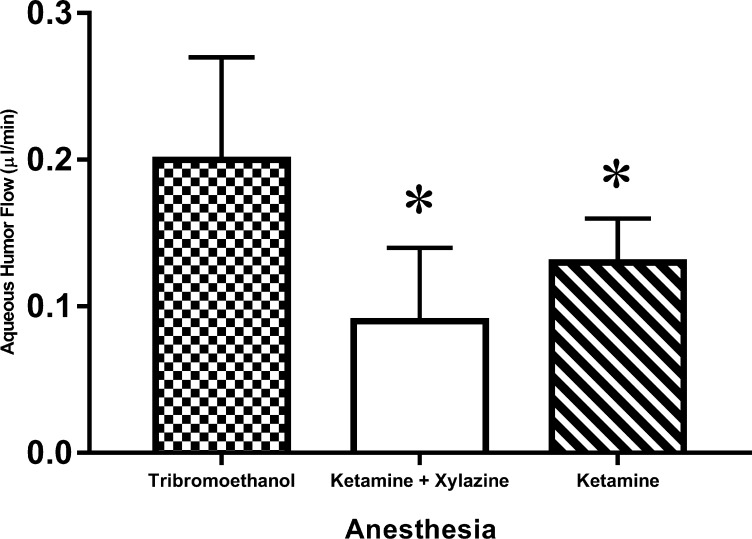
Figure 7.
Effect of anesthesia on aqueous flow measured by fluorophotometry. Aqueous flow as measured by fluorophotometry under ketamine/xylazine anesthesia was 0.09 ± 0.05 μL/min (mean ± SD, n = 21); under ketamine anesthesia was 0.13 ± 0.03 μL/min (n = 10); and under 2,2,2-tribromoethanol anesthesia was 0.20 ± 0.07 μL/min (n = 7). Differences in flow were detected across anesthesia groups (P = 0.001). Ketamine only (P < 0.05) and ketamine/xylazine anesthesia were associated with lower aqueous flow rates than tribromoethanol (*P = 0.001).