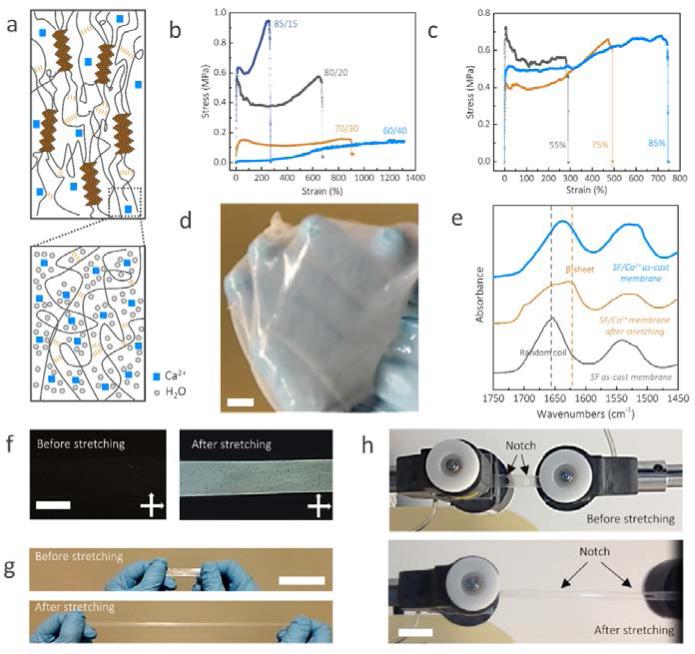
Fig. 2.
Structural and mechanical characterization of the highly stretchable silk membranes. (a) Schematic illustration of the components and interactions of SF/Ca2+ silk membranes. (b) Typical stress-strain plots of SF/Ca2+ membranes at varying SF/Ca2+ weight ratios with the same relative humidity (80%). (c) Typical stress-strain plots of SF/Ca2+ (80/20) membranes after incubation at various relative humidity levels controlled by specific saturated salt solutions with known relative humidity: KCl (85%); NaCl (75%), Mg(NO3)2 (55%). (d) The SF/Ca2+ membranes were stable after immersion in water for 4 hours. (e) FTIR spectra of silk films from 1750 to 1450 cm−1, which includes amide I and amide II bands (1630 and 1655 cm−1 are assigned to β-sheet and random coil, respectively). The black spectrum is the control sample prepared from SF/LiBr/water. The brief preparation process is to dissolve the dry degummed B. mori silk fibers in 9.3 mol/L LiBr aqueous solution. After dialysis against deionized water, the resultant SF solution was cast to obtain SF as cast membrane. (f) Photographs of SF/Ca2+ membranes under cross-polarized light before and after stretching. (g, h) the pictures of un-notched (g) and notched (h) SF/Ca2+ silk membranes before and after stretching. The scale bars are 1 cm.