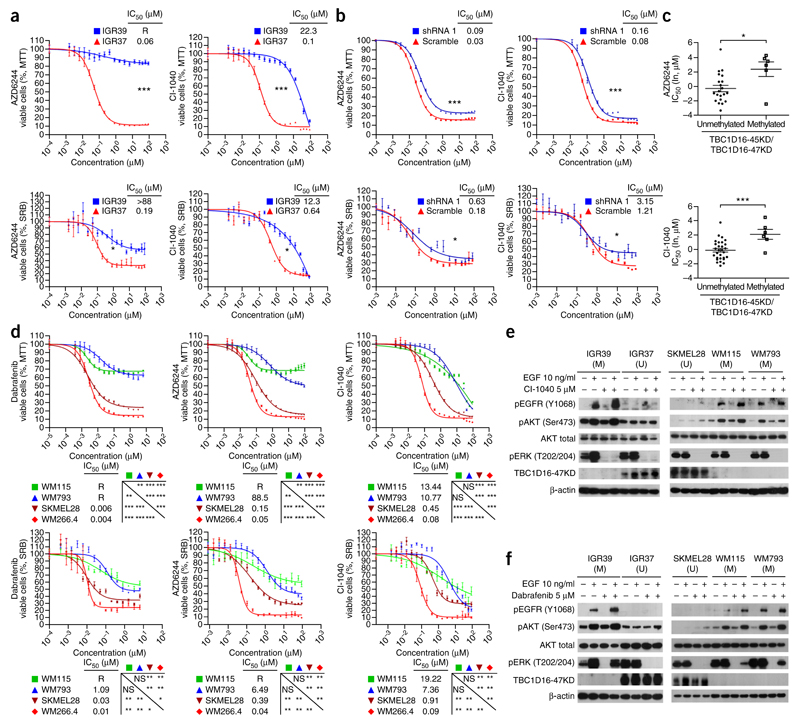
Figure 5.
Epigenetic reactivation of TBC1D16-47KD predicts response to BRAF and MEK inhibitors by targeting two signaling pathways. (a) MTT and SRB assays in IGR37 and IGR39 cells upon treatment with MEK inhibitors (AZD6244 and CI-1040). Corresponding half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values are also shown. R = resistance to drug inhibition. (b) shRNA-mediated downregulation of TBC1D16-47KD induced higher resistance to MEK inhibitors compared with the shRNA-scrambled control cells. (c) TBC1D16-47KD CpG island unmethylated status is associated with enhanced sensitivity to MEK inhibitors in the Sanger panel of melanoma cell lines. y axis, drug IC50 values (natural log, μM); x axis, DNA methylation status. Values are means ± s.e.m. (d) MTT and SRB assays in the WM115 (methylated), WM793 (methylated), SK-MEL-28 (unmethylated) and WM266.4 (unmethylated) cell lines upon the use of BRAF or MEK inhibitors. (e) Western blot analyses of the RAS/BRAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways in TBC1D16-47KD unmethylated (U) or methylated (M) melanoma cells upon using the MEK inhibitor CI-1040. (f) Western blot analyses of the RAS/BRAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways in TBC1D16-47KD unmethylated (U) or methylated (M) melanoma cells upon using the BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib. Significance was determined from a 10,000-permutation t-test with Holm correction of the difference between growth curves. NS, nonsignificant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Error bars show means ± s.e.m.