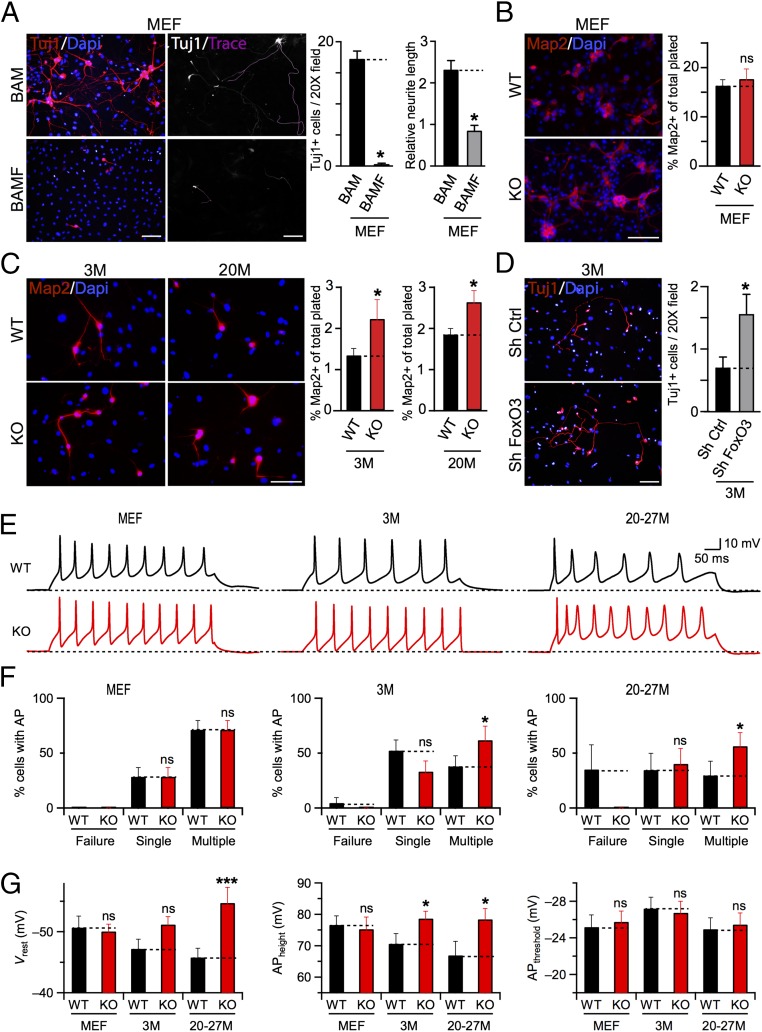
Fig. 4.
Loss of FoxO3 improves reprogramming efficiency and functional maturation of iN cells derived from TTFs but not from MEFs. (A) Tuj1-immunoreactive, traced MEF iN cells derived in control condition (infected with BAM factors only, BAM; Upper) or in the presence of FoxO3 transcription factor (infected with BAM factors + FoxO3, BAMF; Lower). Bar graphs represent average values (means ± SEM, n = 3 batches, *P < 0.05, ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test) of cell number and relative neurite length for each condition, as indicated. (B) Map2-immunoreactive MEF iN cells derived from WT (Upper) and FoxO3−/− (KO; Lower) littermate animals. Average percentages are means ± SEM, n = 3 experiments (*P < 0.05, ANOVA with Bonferoni post hoc test). (C) Same as B, except for TTF iN cells derived from 3M (Left) and 20M (Right) old WT (Upper) or FoxO3 KO (Lower) animals. (D) Representative images (Left) of Tuj1+ iN cells derived from 3M TTF, in the presence of shRNA hairpins for scrambled control (Sh Ctrl; Upper) or FoxO3 (Sh FoxO3; Lower). Average numbers of Tuj1+ cells are plotted as means ± SEM (Right) for each condition, n = 3 technical replicates (*P < 0.05, ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test). (E) Example traces of APs recorded from iN cells derived from MEF (Left), 3M (Center), and 20–27 M (Right) TTF of WT (Upper, black) or KO (Lower, red) mice. (F) Percentages (means ± SEM) of iN cells with no (Failure), single, or multiple APs recorded from MEF (Left), 3M (Center), and 20–27 M TTFs (Right). Asterisks indicate significant difference (n = 3 independent batches, *P < 0.05, Student’s t test) for pairwise comparison (dotted lines). ns, not significant. (G) Average values of the Vrest, AP height, and AP threshold of iN cells derived from MEF, 3M, and 20–27M TTFs (n = 21, 21, and 43, respectively, for each genotype). Asterisks, significant difference (*P < 0.05, ***P < 0.005), ns, not significant, Student’s t test. (Scale bars: 50 μm.)