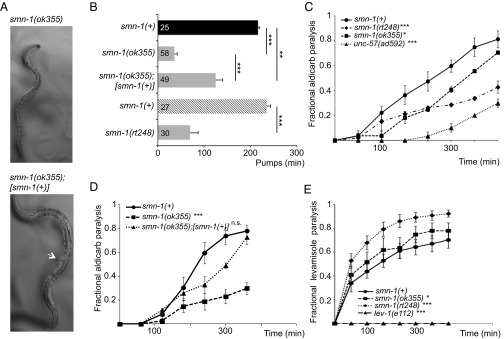
Fig. 1.
Decreased SMN function in C. elegans causes defective motor neuron function. (A) Images of age-matched smn-1(ok355) (Top) and smn-1(ok355);[smn-1(+)] (Bottom) animals. Single-copy insertion of an [smn-1(+)] transgene rtSi10 rescued smn-1(ok355) larval lethality and growth but did not restore fertility. Arrow indicates adult vulva, which has not developed in age-matched smn-1(ok355). (B) smn-1(ok355) and smn-1(rt248) animals had reduced pumping rates vs. respective smn-1(+) controls. Studies in B involving smn-1(ok355) were run independently from studies with smn-1(rt248) but combined into one panel for brevity [black column, smn-1(+) control for ok355; cross-hatched, smn-1(+) control for rt248)]. smn-1(ok355) pharyngeal pumping defects (at day 3 posthatching) were ameliorated by introducing an smn-1(+) rescue construct. Mean ± SEM; Mann–Whitney U test, two-tailed: **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (C) smn-1(ok355) and smn-1(rt248) animals were resistant to the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor aldicarb. Time course for paralysis induced by 1 mM aldicarb in smn-1(+), smn-1(ok355), smn-1(rt248), and unc-57(ad592) young L4 hermaphrodites is shown. unc-57 encodes C. elegans endophilin A; unc-57(ad592) causes inappropriate resistance to aldicarb (43). Log-rank test: *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001. (D) The aldicarb resistance of smn-1(ok355) animals was mostly restored by [smn-1(+)] genomic rescue (rtSi10). Log-rank test: ***P < 0.001; n.s., not significant. (E) smn-1(ok355) and smn-1(rt248) were hypersensitive to levamisole, a nicotinic ACh receptor agonist. smn-1(+), smn-1(ok355), smn-1(rt248), and lev-1(e211) young L4 hermaphrodite paralysis on 0.4 mM levamisole plates is reported. lev-1(e211) animals lack a nicotinic ACh receptor subunit. Error bars indicate ± SEM. Log-rank test: *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001.