Fig. 2.
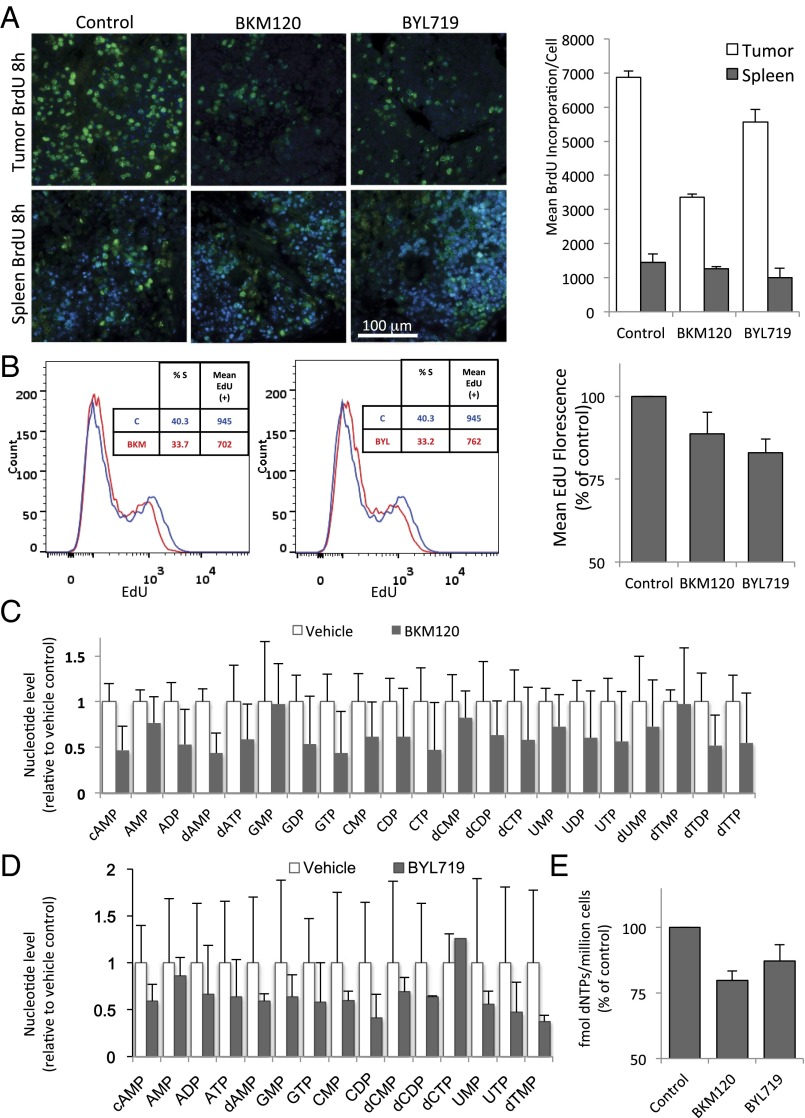
PI3K inhibition leads to a decrease in DNA synthesis of cancer cells within 8 h. (A) K14-Cre BRCA1f/fp53f/f tumor-bearing mice were randomized to drug treatments as indicated and treated for 8 h (two doses, 8 and 2 h before killing). BrdU was given through intraperitoneal injection 2 h before killing. Upon necropsy, tumors and spleens (n = 3 for each group) were harvested, fixed, and stained with anti-BrdU antibodies for immunofluoresence (green). The mean fluorescence per cell of BrdU+ cells was measured by using volocity image analysis software. The bar graph represents mean fluorescence intensity of the BrdU+ cells ± SD. (B) HCC1937 cells were treated for 8 h with drugs as indicated, and EdU was added to the cultures before fixation. EdU was visualized by using the Click-IT technology and analyzed by using flow cytometry. The bar graph represents mean fluorescence intensity of the EdU+ population ± SD of experimental triplicates. (C and D) Determination of nucleotide levels in response to drug treatments in vivo. Tumor tissue from a MMTIV-Cre BRCA1f/fp53+/− (C) or a K14-Cre BRCA1f/f p53f/f tumor-bearing donor mouse (D) was transplanted into the mammary fat pad of NOD/Scid mice (C) or syngeneic K14-Cre− littermates (D) and allowed to grow to 10-mm diameter. Tumor-bearing recipients were then randomized to either control or drug treatment (BKM120 30 mg/kg by mouth or BYL719 30 mg/kg by mouth). Mice were treated 48, 24, and 2 h before killing in C and twice, 16 and 3 h, before killing in D. For raw data, see Datasets S1 and S2. (E) Determination of nucleotide levels in HCC1937 cells after 8 h of drug treatment with either BKM120 or BYL719 by competitive PCR (Materials and Methods).