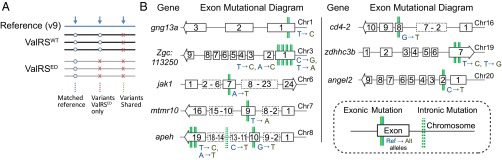
Fig. 5.
Examples of variants in genomes of ValRSED- and ValRSWT-expressing zebrafish, with the replicate filtration strategy used. (A) Three replicate libraries of ValRSWT- or ValRSED-injected p53zdf1/zdf1 zebrafish genomic DNA were sequenced, mapped, processed, and genotyped. The resultant nonreference alleles (variants) that could be found in all three replicates for each sample had a high degree of overlap, and these variants—and many of those specific to the ValRSWT-expressing fish—most likely represent intrinsic differences between the zebrafish strain used in these studies and that of the reference. [In addition, because overexpression of a WT tRNA synthetase, at least in bacteria, can lead to mistranslation (35) and presumably mutagenesis (19), we did not attempt to interpret further the variants specific to the WT fish.] Overall, the sequence match between the WT and reference was greater than 98.5%. The discovered variants were 96% SNPs and 4% InDels. (B) Examples located in specific genes on eight different chromosomes are SNPs that were reliably called as variants in the ValRSED fish and as reference alleles in the ValRSWT fish.