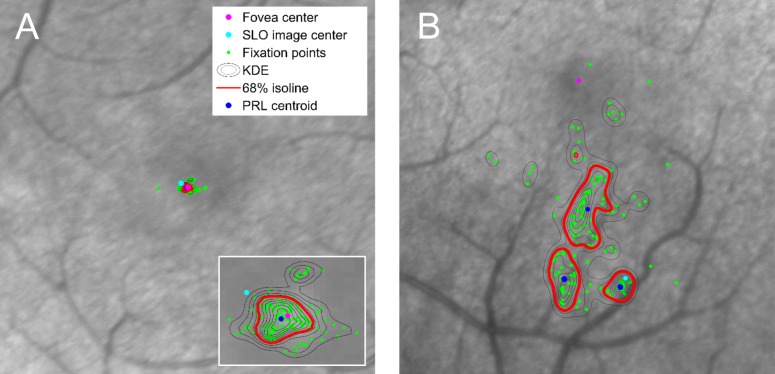
Figure 2.
Comparison of fixation in a normal patient and in a patient with optic neuropathy (larger frames are shown at equal magnification). (A) In a normal patient, fixation occurs within the foveola. Fixation instability, calculated as the area of the 68% isoline of the KDE, equals 0.022 deg2. Fixation eccentricity, measured as the distance between the PRL centroid and the fovea center, equals 0.024°. (B) A patient with LHON and a centrocecal scotoma has eccentric fixation with three distinct PRLs and fixation instability measuring 1.62 deg2. When multiple PRLs are identified, a single measure of eccentricity is calculated by taking an average of the distances between the PRL centroids and the fovea center, each weighted according to the number of fixation points within the corresponding PRL. For this patient, fixation eccentricity was 3.26°.