Figure 1. TssA1 is an essential component of the T6SS apparatus.
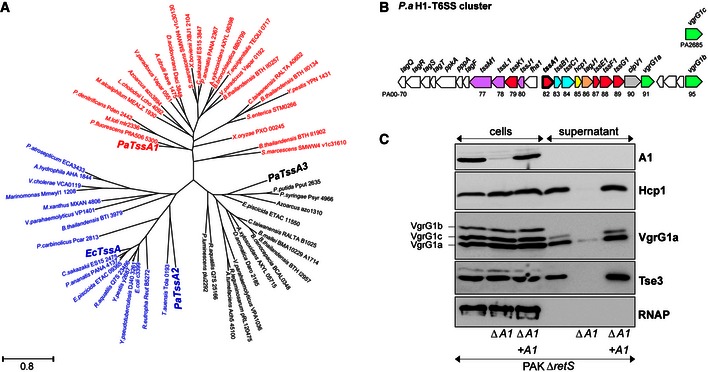
- Maximum‐likelihood phylogenetic tree generated from 61 aligned TssA sequences belonging to the indicated bacterial species. The three TssA proteins from P. aeruginosa (PaTssA1, PaTssA2 and PaTssA3) and E. coli TssA (EcTssA, GenBank accession number: 284924261) are indicated in bold.
- Graphical representation of the H1‐T6SS gene cluster in P. aeruginosa (P.a) (Filloux et al, 2008). The generic tss name and the PA number of corresponding genes are indicated. Genes encoding putative baseplate components are shown in magenta with tssA1 highlighted in bold.
- Proteins from whole‐cell extracts and culture supernatants of PAKΔretS, the derivative tssA1 mutant (∆A1) (both carrying the pBBR plasmid) and the complemented ∆A1 mutant carrying pBBR‐tssA1 (∆A1 + A1) were analysed by Western blot. Polyclonal antibodies directed against TssA1 (A1), Hcp1, VgrG1a and Tse3 were used. The anti‐VgrG1a antibody detects VgrG1a, VgrG1b and VgrG1c, as indicated on the left. Cytoplasmic RNA polymerase (RNAP) was monitored using monoclonal antibody directed against its β‐subunit.
