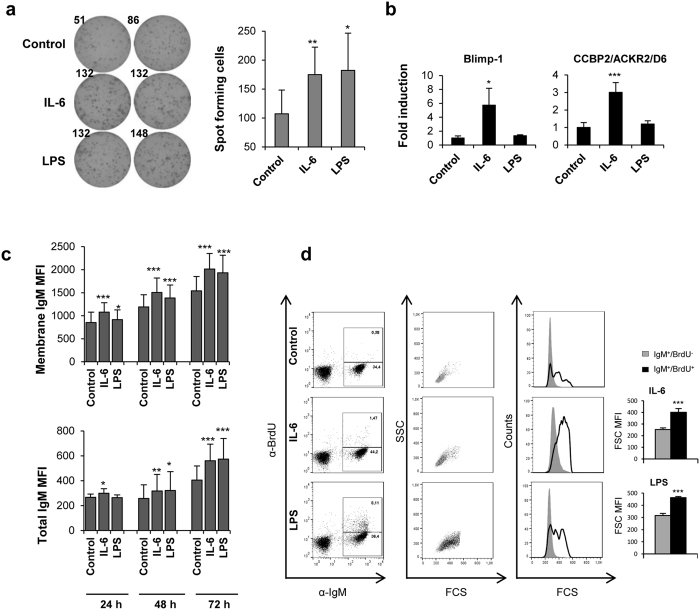
Figure 2. IL-6 and LPS activate IgM secretion in naïve B cells.
(a) ELISPOT analysis of IgM-secreting cells in splenocyte cultures treated with IL-6 (200 ng/ml), LPS (100 μg/ml) or non-stimulated. Splenocytes were cultured for 3 days in ELISPOT plates previously coated with anti-trout IgM mAb (2 μg/ml) in the presence or absence of the different stimuli. After incubation, cells were washed away and a biotinylated anti-trout IgM mAb (1 μg/ml) was used to detect numbers of spot forming cells. Duplicates from a representative experiment (left) and quantification of spot forming cells (right) from 5 independent experiments are shown (mean + standard deviation). (b) Spleen leukocytes were incubated with media containing IL-6, LPS or control media alone for 24 h at 20 °C. After that time, IgM+ B cells were sorted using an anti-trout IgM mAb and RNA was extracted. Relative transcript expression of Blimp-1 and ACKR2 is shown (mean + standard deviation, n = 6). (c) Membrane IgM and total IgM expression of IgM+ cells after incubation with IL-6, LPS or control media for 24, 48 and 72 h. Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) + standard deviation is shown (n = 9). (d) Dot plots and histograms showing the Forward scatter (FSC) from IgM+ B cells and BrdU+/IgM+ B cells incubated in the presence or absence of LPS or IL-6, from one representative experiment. Graphs showing FSC MFI values from 8 independent experiments (mean + standard deviation) are included next to the histograms for stimulated cultures. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.