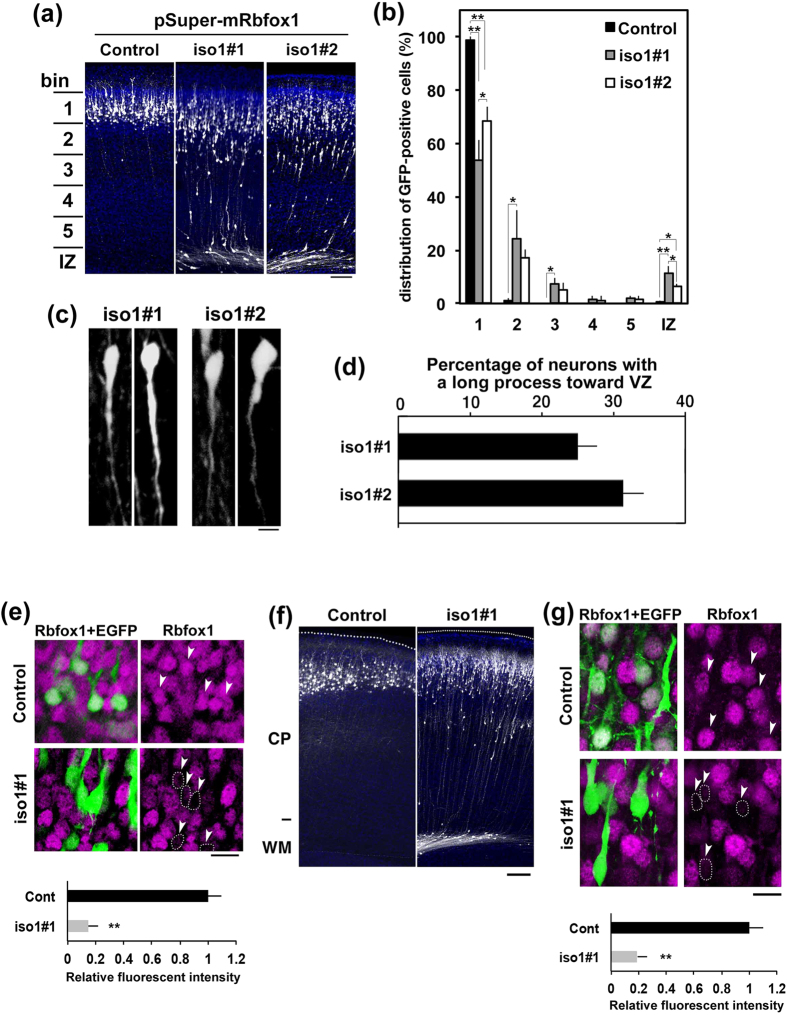
Figure 2. Role of Rbfox1-1 in cortical neuron migration during mouse brain development.
(a) Migration defects of Rbfox1-deficient cortical neurons. pCAG-EGFP was coelectroporated with pSuper-H1.shLuc (Control), pSuper-mRbfox1-iso1#1 or -iso1#2 into cerebral cortices at E14.5. Coronal sections were prepared at P3 and immunostained with anti-GFP (white) and DAPI (blue). Scale bars in (a,f), 100 μm. (b) Quantification of the distribution of the deficient neurons in distinct parts of the cerebral cortex (bin 1–5, and IZ) for each condition shown in (a) Error bars indicate SD (n = 3); **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 by Tukey-Kramer LSD. (c) Representative images of Rbfox1-iso1-deficient neurons remained in CP at P3 under the condition in (a) Scale bar, 5 μm. (d) Quantification of the cortical neurons with a long process toward VZ. Numbers of cells used for each calculation were more than 150 in each condition in (c). Error bars indicate SD. Note that control results are not shown since the control neurons did not show migration delay. (e) Knockdown of Rbfox1-iso1 in vivo in neurons with abnormal positioning. Coronal sections prepared at P3 as in (a) were stained for GFP (green) and Rbfox1 (magenta). Arrowheads indicate GFP-positive cells near the pial surface (Control) or in CP (iso1#1). Rbfox1-deficient cells were encircled by dotted line. Quantification of Rbfox1 expression was performed with ImageJ by analyzing the fluorescent intensity in the control and deficient cells (arrowheads). Scale bars in (e,g), 10 μm. (f) Positional defects of the deficient neurons at P7. In utero transfection was done and coronal sections were immunostained as in (a). (g) Knockdown of Rbfox1-iso1 in vivo at P7. Coronal sections were stained as in (e) Arrowheads indicate GFP-positive cells. Quantification of Rbfox1 expression was performed as in (e).