Fig. 1.
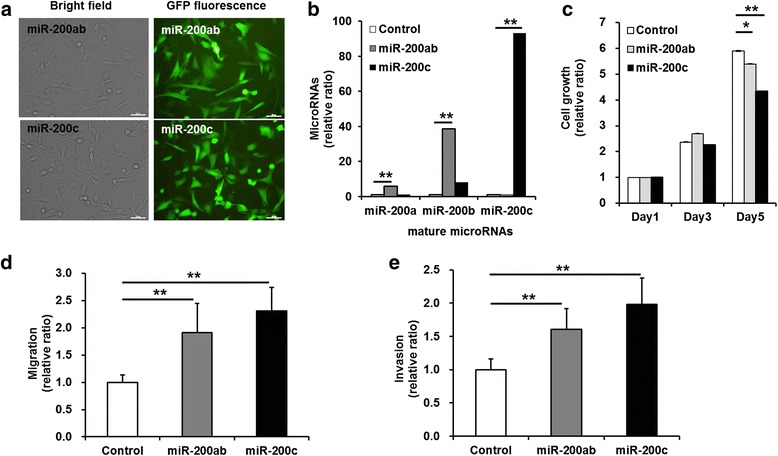
Proliferation, migration, and invasion of miR-200b/200a/429- or miR-141/200c-transduced MDA-MB-231 cells. a Fluorescence images of green fluorescent protein in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells that were transduced using lentivirus encoding both GFP and miR-200 family members. Strong GFP expression was detected in the miR-200 family-transduced cells. Scale bar; 50 μm. b Quantitative real-time RT-PCR of microRNAs (miR-200a, miR-200b, and miR-200c). The miR-200ab cells transduced with the miR-200b/200a/429 cluster construct exhibited high expression levels of miR-200a (~6-fold) and miR-200b (~40-fold) relative to those of the control cells. The miR-200c cells transduced with the miR-200c/141 cluster construct exhibited remarkably high expression levels of miR-200c (~93-fold) and miR-200b (~8-fold) relative to those of the control cells. c MTT assay for analysis of cell proliferation. The growth rate was significantly lower in the miR-200c cells (~4-fold) than in the control cells (~6-fold) at the 5th day. d Trans-well migration assay for the analysis of cell migration. e Trans-well invasion assay for the analysis of the invasive capacity. The migratory and invasive abilities of the miR-200ab and miR-200c cells (~2-fold) were significantly increased compared with those of the control cells. The enhanced migratory and invasive abilities were higher in miR-200c cells than in miR-200ab cells. All experiments were performed at least in triplicate, and the values are the mean values ± standard deviation. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001
