Fig. 3.
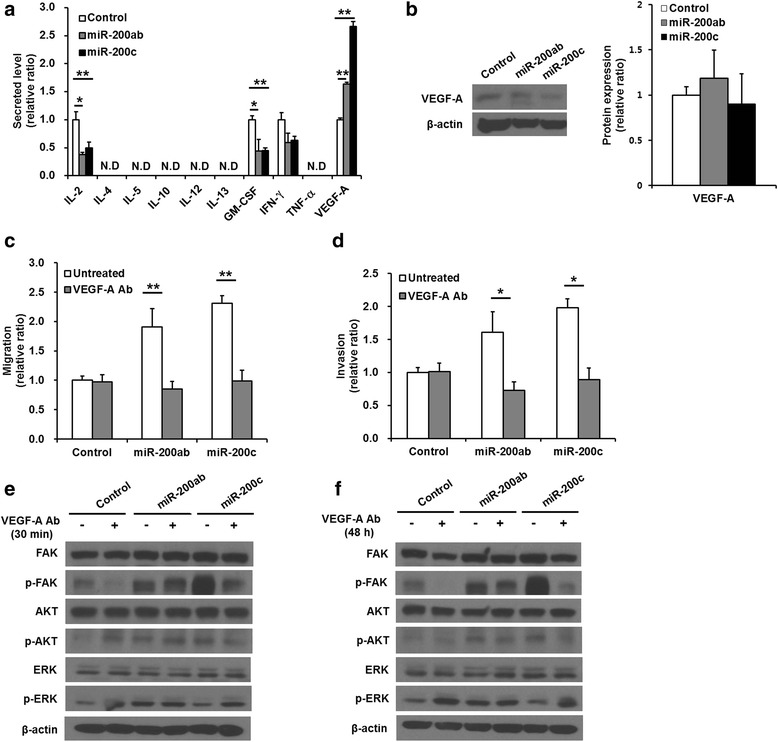
Migration and invasion in miR-200b/200a/429 or miR-141/200c-transduced MDA-MB-231 cells treated with an anti-VEGF-A-neutralizing antibody. a Measurement of the secreted levels of cytokines and growth factors (IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL-12, IL-13, GM-CSF, IFN-γ, TNF-α, and VEGF-A). Transduction of the miR-200 family into MDA-MB-231 cells promoted significantly higher VEGF-A secretion than that of control cells. b Western blotting analysis of the levels of VEGF-A. c Trans-well migration and d invasion assay of anti-VEGF-A-neutralizing antibody-treated cells. The enhanced migration and invasion of the miR-200 family-transduced cells were significantly suppressed by treatment with anti-VEGF-A-neutralizing antibodies. e, f Representative image of western blotting of phosphorylated AKT, FAK, and ERK and total AKT, FAK and ERK in cells treated with anti-VEGF-A-neutralizing antibodies for 30 min and 48 h. The elevated phosphorylation levels of FAK and AKT in only miR-141/200c cluster-transduced cells but not miR-200b/200a/429-transduced cells were decreased by the anti-VEGF-A-neutralizing antibody, whereas the phosphorylation level of ERK was increased in miR-141/200c -transduced cells and control cells treated with anti-VEGF-A-neutralizing antibodies. All experiments were performed at least in triplicate, and the values are the mean values ± standard deviation. N.D: not detectable. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001
