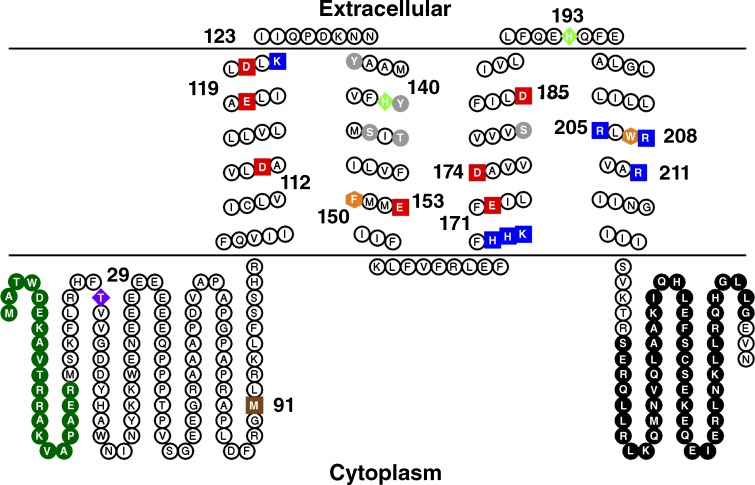
Figure 1.
The amino acid sequence and schematic topology of the human voltage-gated proton channel, hHV1. Within the TM domain, acidic residues are red, basic residues are blue, aromatic residues are orange, and polar residues are gray. Specific amino acids of note, beginning at the N terminus: deletion of 1–20 (green) produces a “short” isoform common in malignant B cells (Hondares et al., 2014); Thr29 is a PKC phosphorylation site responsible for enhanced gating (Musset et al., 2010a); M91T is the first identified hHV1 mutation (Iovannisci et al., 2010); Asp112 is crucial to H+ selectivity (Musset et al., 2011); His140 and His193 coordinate Zn2+ binding (Ramsey et al., 2006); the three Arg in S4 are thought to open the conductance pathway in response to voltage (Ramsey et al., 2006; Sasaki et al., 2006; Gonzalez et al., 2013); and the C terminus has an extensive coiled-coil region (black) that holds the dimer together (Koch et al., 2008; Lee et al., 2008; Tombola et al., 2008; Fujiwara et al., 2014). The image was drawn with TOPO2 (Johns, 2016).