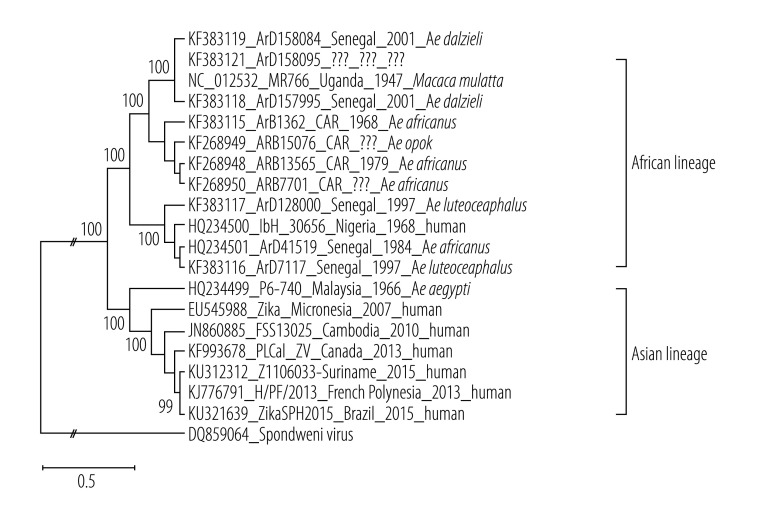
Fig. 2.
Phylogenetic relationships among selected Zika virus strains belonging to the African and Asian lineages based on complete genomic sequence maximum (likelihood analysis)
Notes: The tree was performed with 19 complete sequences available in the GenBank® database (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, USA) as of 21 January 2016, together with a sequence of the closely related Spondweni virus as outgroup. Sequences were aligned using the Clustal W program. The tree was built using the maximum likelihood method with the best fitted parameters calculated in the MEGA version 6.06 software program (general time reversible model with gamma distribution with invariant sites and nearest-neighbour-interchange using a very strong branch swap filter). The sequences are labelled with the following information: GenBank® accession number_strain_country_year of isolation_host. Percentage bootstrap values are indicated at the branch nodes. The scale at the bottom of the tree indicates the number of nucleotide substitution per site.