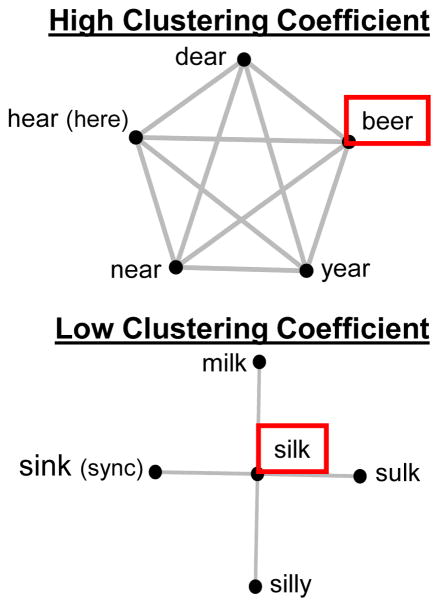
Figure 2.
Sample (not exhaustive) phonological networks of two English words, beer and silk, that differ in their clustering coefficient. Note how the phonological neighbors of beer tend also to be phonological neighbors of each other, resulting in a high clustering coefficient. In contrast, the phonological neighbors of silk are not phonological neighbors, resulting in a low clustering coefficient.