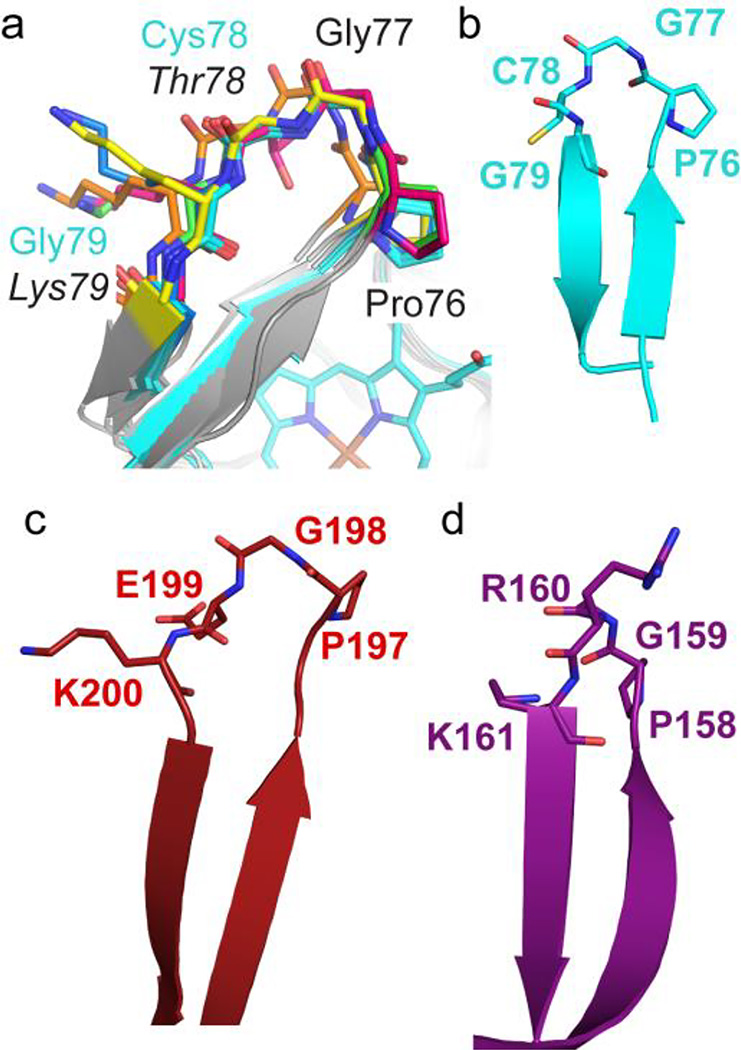
Figure 8.
A conserved stretch of the wild-type cyt c sequence, 76PGTK79, is capable of forming a β-hairpin structure. (a) Backbone analysis of T78C/K79G (cyan) using RosettaBackrub,64 with an in silico-reverted wild-type sequence (indicated by italics), revealed that only minor structural changes are required to produce allowed Ramachandran angles for Lys79, according to MolProbity.108 Ribbon diagrams (gray) with 76P-G-T/C-K/G79 (stick representation in different colors) are shown for five of the ten structures with the lowest predicted energies. (b–d) Using the structural motif PDB searching program, MaDCaT,65 we identified two additional β-hairpin structures similar to that in T78C/K79G (b) with the sequence P-G-X-K. They are: (c) human protein zinc-α-2-glycoprotein (PDB ID: 3ES6),66 with sequence 197P-G-E-K200, and (d) enterobacteria phage 186 repressor protein CI (PDB ID: 2FKD),67 with sequence 158P-G-R-K161. All structures are shown in cartoon and stick representation.