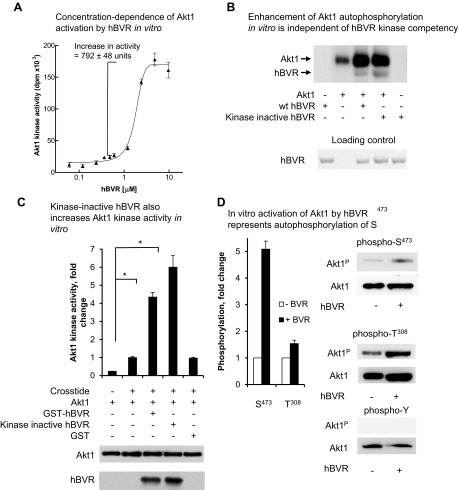
Figure 4.
hBVR activates Akt1 in vitro. A) Concentration dependence of Akt1 activation by hBVR in vitro. Phosphorylation of Crosstide substrate by his6-tagged recombinant Akt1 was measured in presence of increasing concentrations of GST-tagged hBVR. Data were fitted to sigmoid curve using nonlinear regression. B) Enhancement of Akt1 autophosphorylation in vitro is independent of hBVR kinase competency. Autophosphorylation of Akt1 was measured in presence or absence of 2 µg wt or kinase dead (G17 > A) hBVR. Kinase reaction products were separated by SDS-PAGE and detected by autoradiography; loading of hBVR was detected by Ponceau S staining. C) Kinase-inactive hBVR also increases Akt1 kinase activity in vitro. Akt1 activity was measured as in (A) using Crosstide as substrate and wt GST-hBVR, G17 > A kinase inactive mutant, or GST alone. Akt1 and hBVR input is indicated by Western blots. *P < 0.05. D) In vitro activation of Akt1 by hBVR represents autophosphorylation of S473. Akt1 was incubated under conditions favoring Akt kinase activity in presence or absence of hBVR, as described in (C). T308, S473, and tyrosine phosphorylated products were detected by Western blot test by sequentially probing membranes with antibody against specific phosphorylation products, followed by anti-Akt1. Densitometry of T308, S473, and Akt1 blots was used to correct antiphosphopeptide signals for differences in loading.