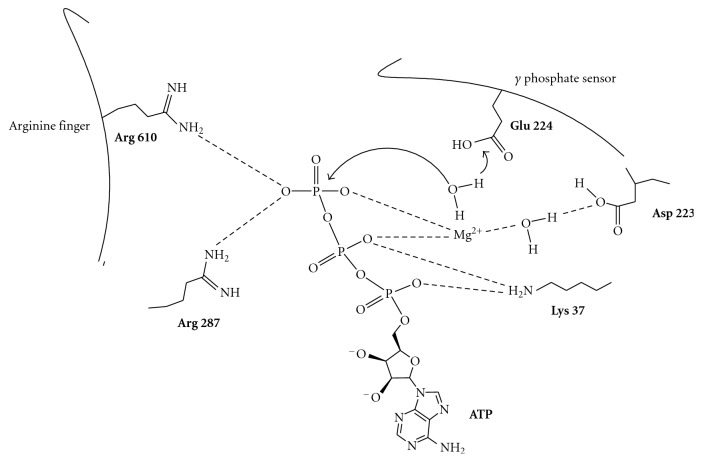
Figure 1.
Mechanism of helicase-catalyzed ATP hydrolysis. Helicases coordinate an ATP, Mg2+ and a water molecule using a conserved Lys and Asp in the Walker A and B motifs on one RecA-like domain and an Arg on an adjacent RecA-like domain. A Glu likely acts as a catalytic base by accepting a proton from the attacking water molecule [11].