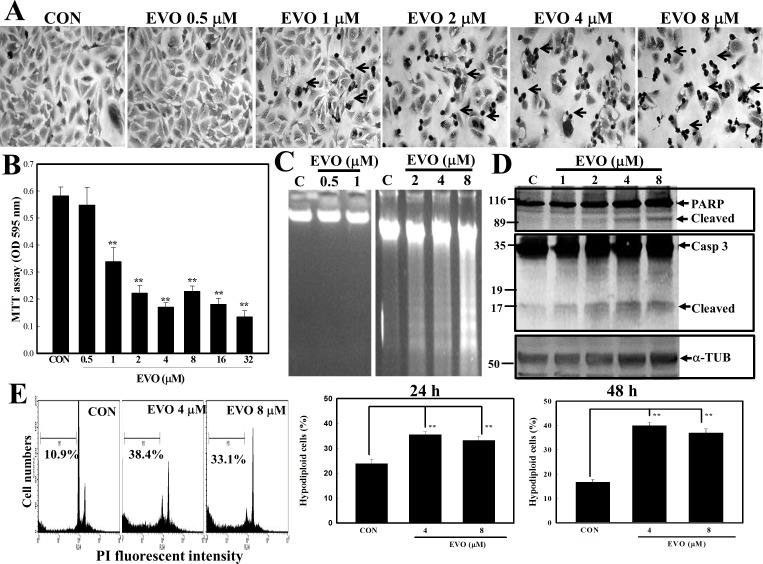
Fig 1. Evodiamine (EVO) reduction of viability of human A498 renal cell carcinoma (RCC) cells via apoptosis induction.
(A) Alterations in cellular morphology by EVO (0.5, 1, 2, 4, and 8 μM) were observed microscopically via Giemsa staining. A498 cells were treated with different concentrations of EVO (0.5, 1, 2, 4, and 8 μM) for 12 h, and morphology of cells was observed microscopically. (B) EVO reduction of cell viability of A498 cells according to an MTT assay. A498 cells were treated with different concentrations of EVO (0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32 μM) for 12 h, and viability of cells was examined by an MTT assay. (C) Loss of DNA integrity with increased DNA ladders by EVO (0.5, 1, 2, 4, and 8 μM) was examined by agarose electrophoresis. (D) EVO induction of cleavage of caspase (Casp)-3 and the PARP protein in A498 cells by Western blotting using specific antibodies. (E) Increased percentage of hypodiploid cells by EVO in A498 RCC cells. Cells were treated with EVO (4 and 8 μM) for 12 h, and the percentage of hypodiploid cells was examined by a flow cytometric analysis via propidium iodide (PI) staining. Each data point was calculated from triplicate determinations, and data are displayed as the mean ± S.D. ** p<0.01, significantly differs compared to the control (CON) group.