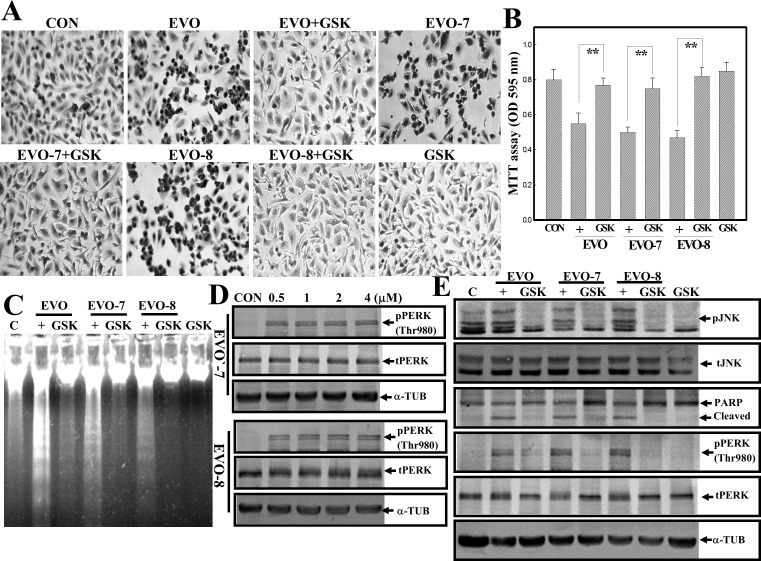
Fig 5. Activation of protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticular kinase (PERK) contributes to evodiamine (EVO)-induced apoptosis of human A498 renal cell carcinoma (RCC) cells.
(A) The PERK inhibitor, GSK, reversed morphological changes by EVOs including EVO, -7, and -8 in A498 cells. A498 cells were treated with or without GSK (20 mM) for 30 min followed by the indicated EVOs (4 μM) for 12 h. The morphology of A498 cells under different treatments was observed microscopically via Giemsa staining. (B) GSK protects A498 cells from EVO-induced cytotoxicity according to an MTT assay. As described in (A), the viability of cells was detected by an MTT assay. (C) GSK addition inhibits EVO-induced DNA ladder formation in A498 cells. As described in (A), the DNA integrity was examined by agarose electrophoresis. (D) EVO-7 and -8 concentration-dependently increased phosphorylation of PERK at Thr980 (p-PERK Thr980) in A498 cells. Cells were treated with different concentrations of EVO-7 or -8 for 12 h, and expressions of phosphorylated and total PERK were examined by Western blotting using specific antibodies. (E) GSK inhibited EVO-, EVO-7-, and EVO-8-induced phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), PERK, and Bcl-2 proteins in A498 cells. As described before, expressions of indicated proteins were examined by Western blotting using specific antibodies. Each data point was calculated from triplicate determinations, and data are displayed as the mean ± S.D. ** p<0.01, significantly differs between the indicated groups (B).